As I am sure you know, Ma’at is the Egyptian Goddess of Truth, Universal Order, and Right. The ideas related to Her form the core of the ancient Egyptian conception of the way things should be. Ma’at was considered to be the very food of the Goddesses and Gods. Ma’at explained the relationships between humanity and the Divine. Ma’at was natural law and social law. Ma’at was not only justice, but also fairness and even kindness toward one another. Ideally, the king who ruled Egypt, the viziers who advised the king, the judges who made decisions that affected the people, and the people themselves all operated under the laws of Ma’at. If they did, peace and plenty and Divine favor would reign in the land.
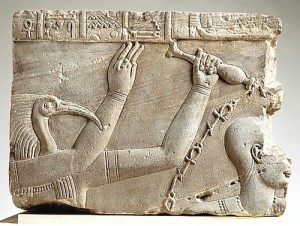
The quintessential symbol of Ma’at is the shut, the ostrich plume that represents the “lightness” and all-pervading, airy nature of Truth and Right. It is against the Feather of Truth that the heart of the deceased is weighed during the post mortum judgment before Osiris. The 42 Assessors Who witness the judgment each hold a Ma’at feather. Following a successful judgment, and as an attestation of their truthfulness, the deceased were sometimes shown wearing Ma’at feathers upon their heads and suspended from their wrists and arms.
Isis, too, is associated with these ideals and sometimes Ma’at is assimilated with Isis. The Osirian Hall of Judgment is also known as the Hall of the Two Truths. Twin Goddesses, the Ma’ati (the Two Truths), presided over it. Very often, the Ma’ati were specifically identified as Isis and Nephthys. (As an aside, I have always found the idea of the Judgment Hall being the place of Two Truths to be a particularly wise concept; there are always at least two sides to any story and both are likely to be true—from the perspective of each participant.)
Without Her twin, Isis was identified with Ma’at’s singular form. The Coffin Texts tell us that Isis comes before the deceased as Ma’at. An inscription at Denderah says that Isis the Great is not only Mother of the God, but also Ma’at in Denderah. Plutarch records a tradition that points to an identification of Isis with Ma’at (“Justice”) in Hermopolis. He writes, “that is why they call the leader of the muses in the city of Hermes at once Isis and Justice, since she is wise…” One scholar has suggested that this Hermopolitan ennead of Muses might have consisted of Isis-Ma’at, Isis-Hathor, and the Seven Hathors.
Isis has always been considered a wise Goddess. A Turin papyrus tells us, “Isis was a woman wise in speech, her heart more cunning than the millions of men, her utterance was more excellent than the millions of gods, she was more perceptive than millions of glorified spirits. She was not ignorant of anything in heaven or earth.” In this aspect, Isis is called Rekhiet, “the Wise Woman.” One of the titles of Isis of the star, Isis-Sothis, is Rekhit, “Knowledge.” This easily led to Isis’ later identification with Sophia (Gk. “Wisdom”). From his Egyptian studies, Plutarch concluded that Isis is a Goddess “exceptionally wise and a lover of wisdom.”
As time passed, Isis’ reputation as a Goddess of Truth, Rightness, Justice, Wisdom, and Law increased. The hymns to Isis at Her temple in the Faiyum oasis say that Isis, “taught customs that justice might in some measure prevail” and that She is “a judge with the immortal gods.” The hymn’s author, Isidorus, writes to his Goddess, “You are directing the world of men, looking down on the manifold deeds of the wicked and gazing down on those of the just” and “You witness individual virtue.” Like Demeter, Isis was called Thesmophoros, “Lawgiver.” A number of Greek inscriptions from Delos and one from Athens calls Her Dikaiosyne, “Righteousness” or “Lawfulness.” Others call Her Nemesis, a Greek justice-bringing Goddess. The ancient historian, Diodorus Siculus, records that “Isis also established laws, they say, in accordance with which the people regularly dispense justice to one another and are led to refrain, through fear of punishment, from illegal violence and insolence…”

In almost all of the surviving Isis aretalogies (self-statements), the Goddess affirms Her connection with Ma’at. In the aretalogy from Kyme, Turkey, Isis says of Herself, “I made the right to be stronger than gold or silver. I ordained that the true should be thought good. I devised marriage contracts. I ordained that nothing should be more feared than an oath. I have delivered the plotter of evil against other men into the hands of the one he plotted against. I established penalties for those who practice injustice. I decreed mercy to suppliants. I protect righteous guards. With me the right prevails.” Similar statements are included in other aretalogies including one from Maronea in Greece, which says that Isis “established justice, so that each one of us, just as he by nature endures equal death, may also be able to live in conditions of equality.” In the late Hermetic texts, both Isis an Osiris are known as lawgivers. One such text, the Kore Kosmou, tells us that Isis and Osiris learned the secrets of lawgiving from God and so became lawgivers for humankind.
The words of the Lady of Words of Power are not only words of magic, but also words of Truth and Justice.
By the way…what inspired me for this post was an interesting article by Christopher Faraone and Emily Teeter that opines that the Greek Wisdom Goddess Metis was either directly or indirectly derived from the Egyptian Goddess Ma’at. (Zeus married, then swallowed, Metis because She was destined to bear Him a daughter Who would be as powerful as Zeus and as wise as Metis—Metis was already pregnant with Athena—and a son Who would be greater than His father. Zeus was not happy with either of those things, so He decided to take Metis into Himself.)
Faraone and Teeter argue that 1.) both Metis and Ma’at were understood as concepts and personified Goddesses 2.) The fact of Zeus swallowing Metis may derive from the Egyptian idea that the Deities “lived on” and “ate” Truth (Ma’at) 3.) Both Metis and Ma’at legitimate the kingship 4.) Just as Egyptian kings had Ma’at names among their coronation names, so Zeus has a number of epithets that include Metis. Interesting, isn’t it?






















































































































 As the days grow longer, a certain soft joy fills me.
As the days grow longer, a certain soft joy fills me.