If you missed getting an Isiopolis post during the last couple of weeks, I have a very good excuse.
I was in Egypt. Finally.
And yes, it was amazing. On multiple levels.
Those of you who have already visited Our Lady’s homeland know. Those of you who haven’t yet, I hope you’ll be able to make the journey someday.
Now, if you’ve been reading along with this blog, you might know that I’ve never been overly interested in the kings and queens of ancient Egypt. For me, it’s always been about the Deities. And one in particular.
Given that, I’ve never been super-fascinated with the pyramids—other than by the sheer fact of their ancient eminence. But if one goes to Egypt, one must, of course, visit the very impressive pyramids.
But I hoped to make this pyramid trek special because of something I learned about years ago and now would have the opportunity to see for myself.
You see, what I’d learned was that there are the remains of a small Isis temple behind one of the queen’s pyramids, behind the Great Pyramid.
The temple is at the pyramid of Henutsen, who was probably the second or third wife of Khufu, and who lived during the fourth dynasty of the Old Kingdom.
There is some confusion over whether Henutsen was a wife or daughter of kings due to an important artifact found in the Giza plateau known as the Inventory Stele. The Stele calls her “king’s daughter” (some Egyptologists think she might have been a daughter of Sneferu). But other than the Stele, the only title we have a record of for her is “king’s wife.” Either way, Henutsen was royalty, bore at least two princes, and got her own smaller pyramid. For our trip, we arranged a private tour in order to be able to include the Isis temple (and forego the camel ride).
Yet, before we talk further, I’d like to quote the Inventory Stele for you, so you can see what is so interesting about it. The Stele has caused a lot of excitement, especially among those who believe that the Sphinx and Pyramids are older than the fourth dynasty period to which Egyptologists usually attribute their construction.
Here’s what it says (my capitalization of Divine pronouns):
Live Horus, the Mezer, the King of Upper and Lower Egypt, Khufu, given life. He made for his mother Isis, the Divine Mother, Mistress of the Western Mountain [i.e. the necropolis], a decree made on a stele, he gave to Her a divine offering, and he built Her a temple of stone, renewing what he had found, namely the Gods in Her place.
Live Horus, the Mezer, the King of Upper and Lower Egypt, Khufu, given life. He found the House of Isis, Mistress of the Pyramid, by the side of the cavity of the Sphinx, on the northwest side of the House of Osiris, Lord of Rostau, and he built his pyramid beside the temple of this Goddess, and he built a pyramid for the king’s daughter, Henutsen, beside this temple. The place of Hwran-Hor-em-akhet [that is, the Sphinx] is on the south of the House of Isis, Mistress of the Pyramid, and on the north of Osiris, Lord of Rostau. The plans of the Image of Hor-em-akhet were brought in order to bring to revision the sayings of the disposition of the Image of the Very Redoubtable. He restored the statue all covered in painting, of the Guardian of the Atmosphere, who guides the winds with his gaze.
He made to quarry the hind part of the nemes headdress, which was lacking, from gilded stone, and which had a length of about 7 ells [3.7 meters]. He came to make a tour, in order to see the thunderbolt, which stands in the Place of the Sycamore, so named because of a great sycamore, whose branches were struck when the Lord of Heaven descended upon the place of Hor-em-akhet, and also this Image, retracing the erasure according to the above-mentioned disposition, which is written {…} of all the animals killed at Rostau. It is a table for the vases full of these animals which, except for the thighs, were eaten near these seven gods, demanding {…} (The God gave) the thought in his heart, of putting a written decree on the side of this Sphinx, in an hour of the night. [That is, the pharaoh had a dream from the Sphinx that he should do this.] The figure of this God, being cut in stone, is solid, and will exist to eternity, having always its face regarding the Orient.
Translation from The Sphinx: Its History in Light of Recent Excavations, Selim Hassan (1949). Hassan takes it from French Egyptologist Gaston Maspero’s original translation.
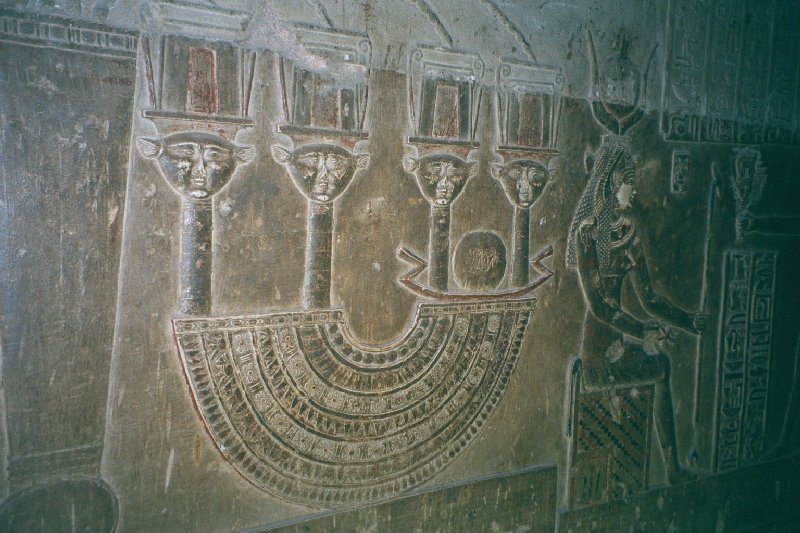
The rest of the stele is taken up with a list of the sacred images of the Deities that Khufu restored within the Temple of Isis. The largest part of the stele is an inventory of these images, which is why it is known as the Inventory Stele.
Pretty cool, huh?
What excited me, of course, were the Isis references and the (new-to-me) title “Mistress of the Pyramid.” What excites most of those who get excited about this stele is that it—supposed to have been carved by Khufu’s fourth-dynasty sculptors on the king’s orders—tells us that the Sphinx was already there by that time! Not only that, but apparently the Temple of Isis was there even before Khufu built his Great Pyramid. So wow, right?
Alas, most Egyptologists agree that the Stele is an archaized work, probably created sometime between the 25th and 26th dynasties, during a period when Nubian kings were trying to revitalize Egypt by harking back to its Old Kingdom glory days. The style of art and writing point most clearly to the 26th dynasty. Key to the evidence is that we have no reference to “Hwran” and “Hor-em-akhet” as names for the Sphinx until the 18th dynasty.
As for the Temple of Isis, it was probably originally a funerary chapel associated with the pyramid of Henutsen, Khufu’s wife, or as the Inventory Stele says, “king’s daughter.” The temple had been “found” by the pharaoh Pasebekhanu in the 21st dynasty and either converted into a small Temple of Isis at that time or, because the pharaoh either had or believed he had found the remains of an earlier Isis temple, had it refurbished as one. There, Isis was worshiped as Lady of the Pyramid until the Roman period. We even have evidence that Her cult had its own priesthood.
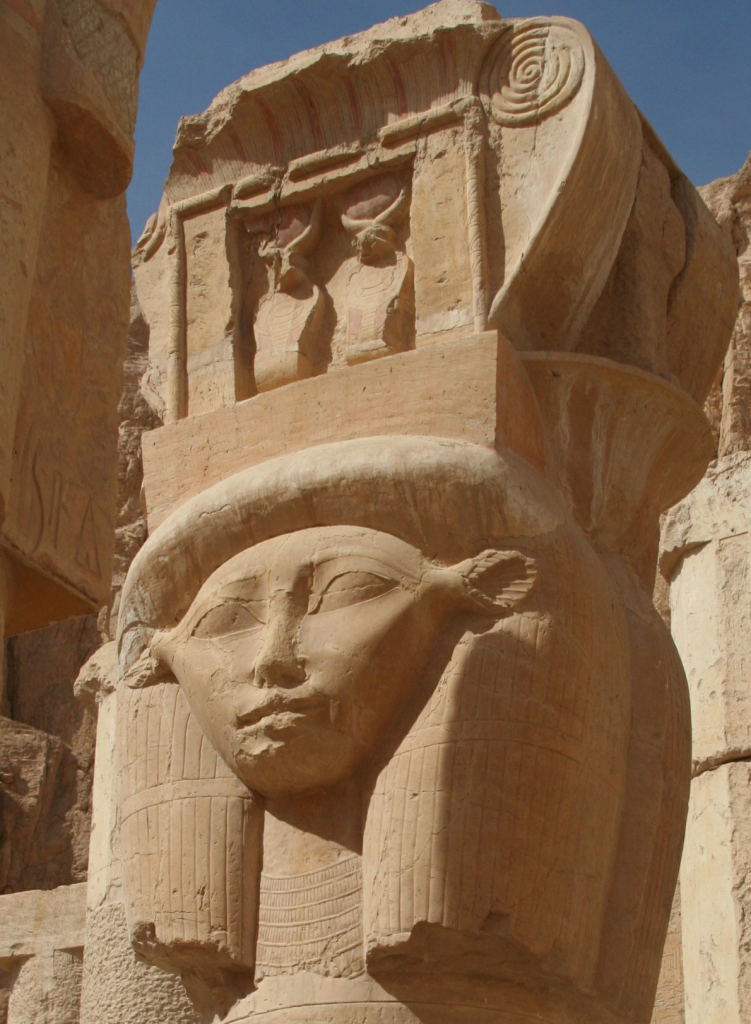
Prior to the Inventory Stele, we find Isis on a Giza stele of Prince Amenomopet, a prince of the 18th dynasty. This is on the so-called Stele C found in the Sphinx Temple and which shows the Sphinx and Isis, wearing the Horns and Disk Crown and within a shrine, receiving offerings from the prince. The image is captioned, “Isis, the Great, the Divine Mother, Queen of the Gods, One in Heaven, Who Has No Equal, the Elder [daughter of] Atum.” Dating on the stele is controversial (so what else is new in Egyptology?), but if the 18th dynasty dating is accurate, then Isis and the Sphinx are being worshiped together at Giza by at least that time.
After this period, we have a number of other Giza inscriptions that include Isis. Some that list Her with other Deities, notably Osiris and Horus, some that indicate that She was being worshiped alone. So it would seem that there was an active cult of Isis at Giza from at least the 18th dynasty. There is also evidence of private devotion at the Temple of Isis; a number of votive plaques were found there as well. (By the way, this info has been gathered together by Christiane M. Zivie-Coche in her book Giza Au Premier Millenaire Autour du Temple D’Isis, Dames des Pyramides.)
We also have several fragments of columns, probably from the Ramessid era, but which were reused in the Third Intermediate Period by Pharaoh Amenemope, on which the king offers wine to Osiris and Isis, Who is identified specifically as Lady of the Pyramids. Because the column was reused, we can’t be sure whether that epithet goes back to the Ramessid period or is from the 21st dynasty. Either way, we have another attestation that one of the Goddess’ epithets is Mistress or Lady of the Pyramid (or Pyramids). This likely refers to Her function of protecting the pyramids and the Osiris-kings in them, and surely to Her power to safeguard their rebirths as well.
Interestingly, a graffito on Henutsen’s pyramid from (probably) Egypt’s late period says that the pyramid is the burial place of Isis. Oriented to the south, it faced the symbolic burial place of Osiris, Lord of Rostau.
I’m looking at another article about all this that leans toward taking the Inventory Stele more seriously as fact than previously thought. If there’s anything of interest there, I’ll let you know. But I think this is enough for now.
I am privileged to have been able to sit at Her Giza temple. There’s not much left, either in temple structure or (unfortunately) residual magical buzz. But that’s okay. For I’ll use what I experienced in Giza in my meditations in Her shrine here. I’ll add Her epithet of Mistress of the Pyramid to Her names honored here. In time, Her pyramidal Mysteries will unfurl once more.