We know quite a lot about the history of the Great Goddess Isis. For instance, we know that She was already important by the time of the Pyramid Texts (Old Kingdom, 5th-6th dynasties). We know fairly clearly how Her worship spread throughout Egypt. We know how She came into Nubia and the Mediterranean. And we know how She went underground with the rise of Christianity in the Mediterranean and the West…staying alive in the magical traditions. Today there are few who do not at least know Her name.
Yet, what we don’t know for certain is where Her worship originated. So far, it is one of Her Mysteries.
Oh, there are theories. The one I am most seeing lately is that She is originally from some small city in the Egyptian delta of Lower Egypt. But I’ve haven’t seen the arguments to back that up. And strangely, no town in ancient Egypt, Upper or Lower, claimed to be Her “birthplace.” Since She became Egypt’s most famous Goddess, you would think someone would claim Her as their own.

Others attribute Upper Egyptian origins to Her, especially given Her important Upper Egyptian temple at Philae (now on Agilkia island). However, the oldest evidence we have of Isis worship on Philae is from the 26th dynasty.
On the other hand, the consensus of researchers today is that what would become ancient Egypt was first populated by Paleolithic people moving from south to north. So if proto-Isis was already known to these people, perhaps She did come from what would eventually be Upper Egypt. And Abydos, an important Osirian cult center, is in Upper Egypt.
On the other, other hand, Isis and Osiris are incorporated into the Heliopolitan myth cycle. And Heliopolis is about 20 miles north of Cairo and in the delta. What’s more, there was another famous Isis temple right there in the middle of the delta at Isiopolis. We may eventually find that it (or its predecessor on the site) is, in fact, the oldest temple of Isis. (Yes, of course, I asked Her. She told me, “delta.” But that is decidedly UPG, “unverified personal gnosis.”)
I recently came across a paper by Dr. Kelly-Anne Diamond, an Egyptologist currently serving as Visiting Assistant Professor in the History Department at Villanova University, that makes a new and interesting contribution to the possible origins of Isis. She focuses in on the title of a female funerary ritualist. The title is “demdjet” and she can appear as a human ritualist, but also sometimes as a Divine ritualist. We find her—very infrequently—from the Old Kingdom to the New. Egyptologists used to group this ritualist under the general category of “mourning women,” but it appears the demdjet or Demdjet may have had a more specific function.
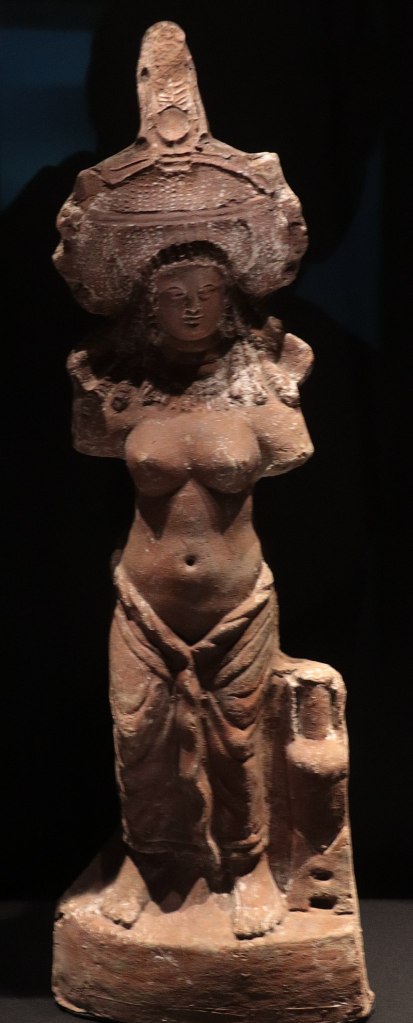
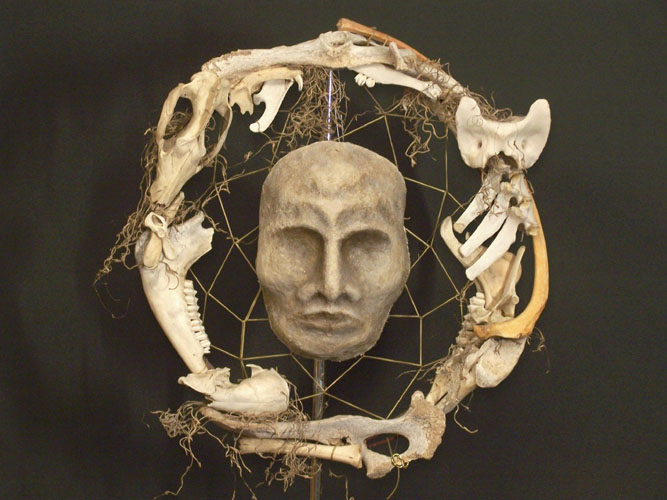
The root of the word has to do with collecting or assembling. And since the title is a feminine active participle, the title demdjet is “she who collects or assembles.” If you’re at all familiar with the ancient Egyptian funerary texts, you may recall that there is quite a lot of emphasis on making sure the deceased have all their bones, bits, limbs, heads, etc. collected or assembled for them as well as ensuring none of those things are disassembled or lost. Since Isis is the collector of bits and pieces par excellence, at least when it comes to Osiris (and the deceased), Diamond suggests that this ritual role may play a part in Isis’ origins.
One of the Pyramid Texts (PT 2283) refers to a Demdjet Vulture. It says, “Osiris Neith, accept Horus’ Eye, which Seth hid—THE HIDDEN VULTURE, which he joined—THE JOINED [Demdjet] VULTURE…” This Demdjet Vulture is involved with stretching or spreading something. We cannot say whether the Demdjet Vulture is supposed to be Isis, but at least we may have an early attestation of a Divine Demdjet. Of course, Isis can take vulture form, but it is not Her most common bird form.
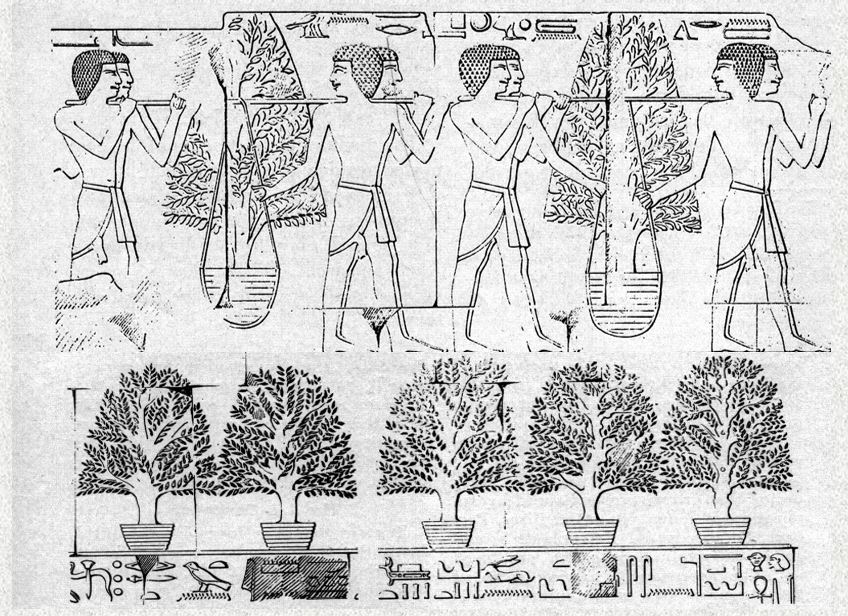
We also find the Demdjet in the pyramid temple of Senwosret III where She gives life and protection. From the Middle Kingdom, there are demdjets in the papyrus Ramesseum E. Some scholars think that the contents of that papyrus may date back to the 3rd dynasty (there are archaisms in the text). If true, it would be the oldest mention of a demdjet.
In this papyrus, we learn that the demdjets are present throughout the funerary rites. At some point, the demdjets move simultaneously, perhaps in ritual motion or dance. They are there when the deceased is summoned to revivification. And they have speaking parts. In the New Kingdom, we have several more instances of demdjets. They are shown as two kneeling women with nu water pots and they are watering “the desert necropolis.” In one case, one woman is labeled menkenu and one demdjet. (Alan Gardiner suggests menkenu is a title of Isis, while demdjet is a title of Nephthys.) In another case, one is called demdjet and one is called kenut (menkenu and kenut may be different versions of the same title).
But here’s where it gets more interesting for Isiacs. In the last New Kingdom example (tomb of Paheri, if you must know), we find the same scene—women kneeling with nu pots, dressed in the same way—but this time, They are labeled Djeret Weret (Great Kite) and Djeret Nedjeset (Lesser Kite). In this time period, we know Who the Great Kite and the Lesser Kite are; They are Isis and Nephthys. So, the women depicted may be human ritualists portraying the Goddesses, which we know was done in Egyptian ritual. In additional, but very damaged, scenes in two of these tombs, we see the demdjet no longer kneeling, but standing with her/Her right arm raised, elbow bent, and fist clenched while her/Her left clenched fist is placed at her/Her chest. It reminds me of the henu gesture, but standing.
She is labeled Djeret Weret Demdjet, the Great Kite Demdjet. The gesture s/She makes is thought to be associated with transfiguration, the recitation of holy words, and glorifications for the dead.
In the Book of the Amduat, a Goddess named Demdjet appears in the 7th and 8th Hours of the Night where She helps protect Re and the Sun Barque as it journeys through the Otherworld. In the 7th Hour, She is with three other Goddesses: She Who Cuts, She Who Punishes, and She Who Annihilates. In the 8th Hour, Demdjet is with three other mummiform Goddesses: She Who Veils, She Who Decorates (?), and the Dark One. Interestingly, the 7th Hour is the same Hour in which Isis and the Elder Magician work Their powerful magic to subdue Apophis. So in this case, with Isis in Her Great of Magic form, it seems to me it would be a bit of a stretch to consider this Demdjet, a minor Hours Goddess, to be a form of Isis.

Nevertheless, with its core meaning of She Who Collects, Assembles, and Puts Together, we can find in the Demdjet an important harmony with one aspect of Great Isis: She Who searches, finds, reassembles, and gives new life to Osiris.
Some researchers have suggested that there may have been a very early Egyptian funerary custom in which important dead persons were disarticulated and then put back together for rejuvenation. It’s a highly controversial topic, but if so, perhaps the original Demdjet may have been the female ritualist who did this reassembly. Perhaps she was serving as a priestess of the Great Renewing Mother. And perhaps, just perhaps, this Great Mother Regeneratrix was the Demdjet Weret—(proto) Iset Demdjet—She Who collects our bones for us that we may be made whole in preparation for our rebirth.