This week got away from me.
I’ve been working on some new material for the new edition of Isis Magic (yay!). But that means I didn’t get to the post I was planning for today—some juicy tidbits about Isis in Rome (She’s still there, of course).
Instead I’m reposting the story of when I knew Isis had accepted me. I’d love to hear you story, too. Please do share in the comments, if you’d like.
I am terrible with memories. I don’t mean my memory is bad. I mean I don’t honor ‘things past’ enough. I don’t take many pictures (and certainly not of myself). I tend not to care for traditional souvenirs. And I definitely have the “get rid of it” gene (which my beloved does not). In my defense, I don’t generally dwell on past wrongs either.
Earlier this week, this post was going to be on an entirely different topic. But then I came across an old magical journal. And there were memories in it.
I do keep magical journals. I don’t record everything all the time (good Goddess, the paper trail would never end!). Usually, I keep them during periods when I’m doing a lot of magical work. This particular journal, as I have said, is old. I mean really old. Like “before the fire” old. Yes, of course, you don’t know what I mean.
Before we moved to the Pacific Northwest, we lived in an apartment in Tennessee. One night the complex caught on fire. Neighbors knocked on neighbors’ doors, telling them to get up and get out. We grabbed the cat and the insurance papers and got out. The next day, with the fire quenched, we were able to go back to survey the damage. It had been a weird fire. Things like our stereo system were completely and utterly incinerated. Things like our irreplaceable magical papers (papers!) were saved. This journal was among them. I can tell from the singed edges.
So I thought I’d sit down and read it. There was lots of visionary work pertaining to a magical system I was training in. But every now and then, there were entries about Isis. This was before I knew very much about Her, before I became Her priestess, and way before Isis Magic. Yet I clearly had been working with Her (or She was working with me).
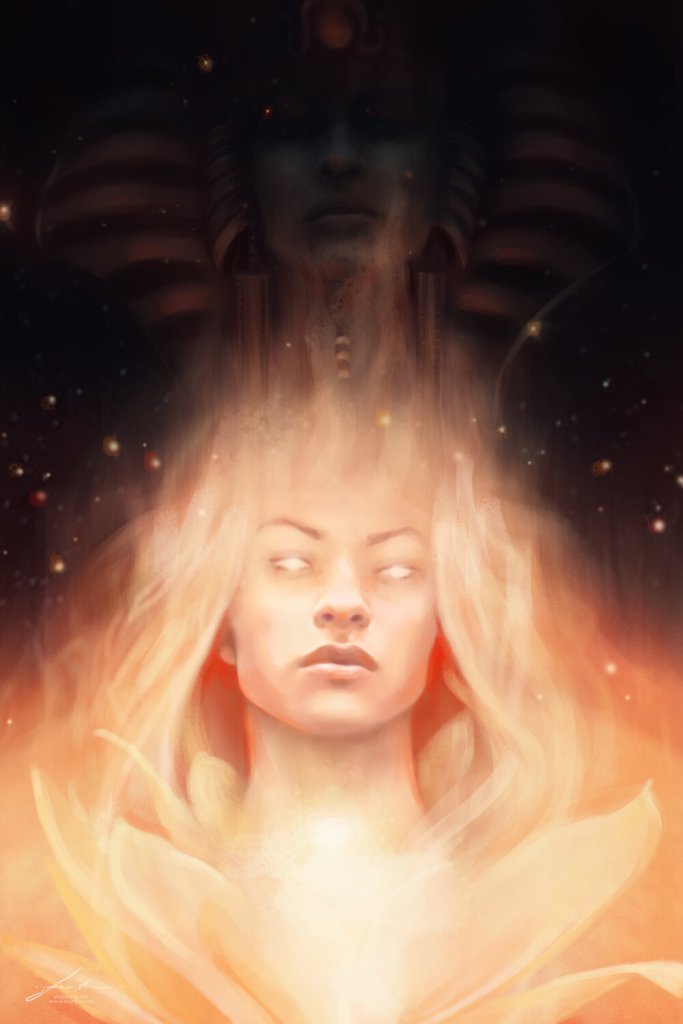
One entry reads, “I have had a very strong Isis connection since my dream the other night.” That dream was not recorded, but a vision was. I was working on love and acceptance. For the vision, I called on Isis to touch me and help me let Her love of humanity come through me. I sensed Her great, but gentle hand descend from above. She placed it on top of my head. Waves of Her not-quite-orgasmic love passed though me and out into the world. I describe that flow of energy, then write, “I again saw the bright, bright, blue glowing lotus.” It had been so bright that I couldn’t tell one petal from another; eventually, the lotus-light enveloped me. I conclude, “I am feeling very worshipful of Great Isis.”
I see myself falling in love with Her through this journal.
Another entry says, “A most wondrous dream! A prayer answered!” Apparently, my beloved was snoring, so I took my bedding and went into our temple room to sleep. I was overcome with a desire to know, truly know, that Isis was with me. I write that it was “a demanding, revealing need” for Her presence. I prayed to Her “more emotionally than ever before” to send a dream to let me know She was with me. I chanted Her name for a while, then slept.

“A few hours later,” I write, “I came from a full, deep sleep to awake with loud sobbing from happiness and amazement.” (My sobbing.) Due to the abrupt awakening, I lost part of the dream. But the actual content of the dream wasn’t the point. The point was that, in the dream, the resolution to a dream-problem happened by a miracle. By Her miracle. And it made me so happy that I woke up crying with joy. And I again saw the blue lotus flower.
I remember this event. The details are a bit fuzzy now, but I vividly remember the visionary blue lotus. I could see it anytime I closed my eyes with crystal clarity instead of the vague dreaminess that vision often has. “I must look up lotus symbolism and I must make a blue lotus talisman,” I wrote. See how much I didn’t know then? Another entry says simply, “I love Her.” And now you know why the Isis temple in my backyard is called the Lotus Temple.
Next, I found an entry that I had marked IMPORTANT with a drawing of a star, a lotus, and a sickle on top. I wrote, “In the dark month of February, on the 15th of the month, with the moon waning in Capricorn, I have taken and been taken by Isis in Her Black Aspect as my Lady, my personal Goddess.” But this wasn’t when I became Her priestess; that was long in the future then. This was my forming a true bond with Her, a bond that will last my entire life. She became “my” Goddess, I became Her devotee. This is when I really began learning about Her.

There is, of course, more in this journal. I see my own inner struggles, doubts, fears, angers, and depression. But this particular record is incomplete. These are loose-leaf pages without a binder…and it seems that some are missing. After we moved to Portland, I began buying blank-but-bound books for my journals. The next one—which I am still writing in—starts with the time when I actually did become Isis’ priestess. In this journal, I can see that I am working out the magic part for what will eventually become Isis Magic.
But I think I have regaled you with quite enough of my journal entries for now. And I have learned my lesson that I should better value memories and keepsakes. Perhaps you will do some magical work with Isis yourself today? After all, your story will be a much better tale—because it will be yours. Just don’t forget to write in your journal.