It’s that time of year when we (once again) see all those articles comparing the Divine Mother Mary with the Divine Mother Isis, followed by either outrage or approbation, depending on who’s doing the writing.
Recently, in relation to this, a friend of this blog asked a very excellent question. It had to do with Isis’ status as a Virgin Goddess. Basically, is She or isn’t She? She is often compared with the famously Virgin Mary, and the images of the two Goddesses, nursing Their holy babes, are strikingly similar. And then there’s all of this.
Well, as is often the way with Goddesses, the answer is both no and yes.
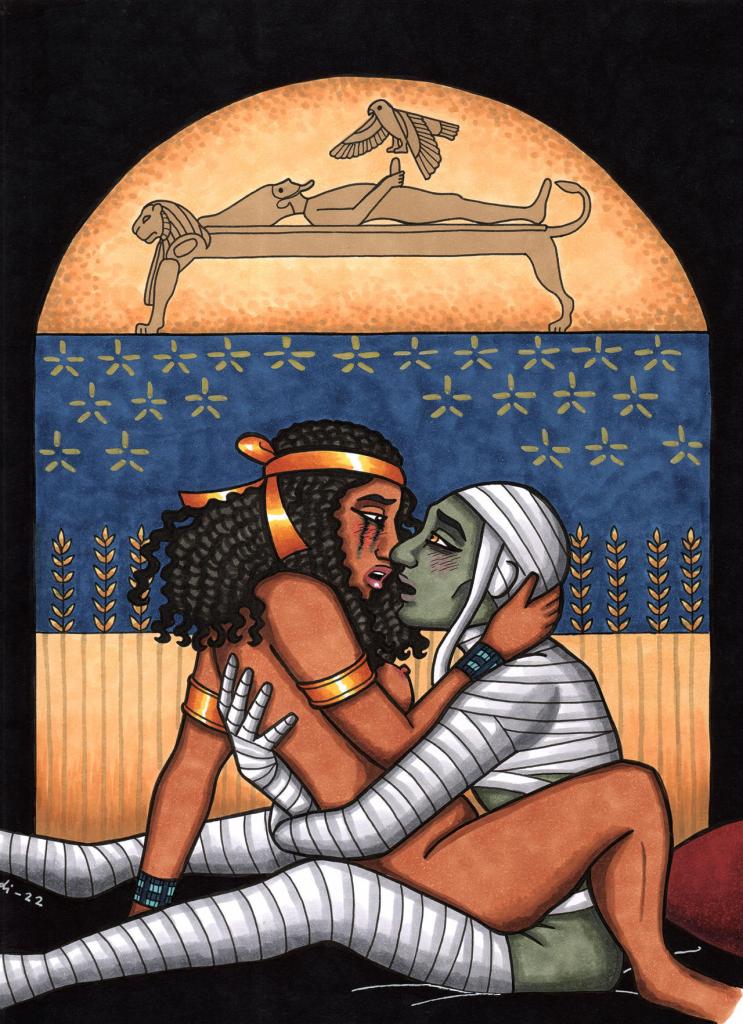

We’re all pretty familiar with the sexual relations between Isis and Osiris. All the way back to the Pyramid Texts we hear about it, rather explicitly we might add. Pyramid Text 366 says, “Your [Osiris] sister Isis comes to You rejoicing for love of You. You have placed Her on your phallus and Your seed issues into Her…” Plutarch, in the version of the story he recorded, tells us that Isis and Osiris were so in love with each other that They even made love while still within the womb of Their Great Mother Nuet. And, of course, we have the sacred story of how Isis collected the pieces of the body of murdered-and-dismembered Osiris, all except the phallus. Crafting a replacement of gold, the flesh of the Gods, She was able to arouse Her Beloved sufficient for the conception of Horus. The mourning songs of Isis and Nephthys have Her longing for His love. The priestess, in the Goddessform of Isis, sings that “fire is in Me for love of Thee” and She calls Him Lord of Love and Lord of Passion. She pleads, “Lie Thou with Thy sister Isis, remove Thou the pain that is in Her body.” (For more on the Songs or Lamentations, go here.)
So, is that all there is to it? Isis is not a virgin?
Well, not quite. Because Isis is a Goddess.
Isis is the Goddess of 10,000 Names and 10,000 Forms. Among those forms are the sexual Lover of Osiris and the Mother of Horus. Among Her many Names are syncretisms with famously virginal Goddesses such as Artemis, Hekate, and Athena, as well as heroines such as Io, a virgin priestess of Hera (a Goddess Who Herself renews Her virginity on the regular). Isis is identified with both Demeter the Mother and Persephone the Kore, the Young Girl, Who were sometimes seen as a single unit, Mother-Daughter, containing All in Themselves. Goddesses can be many things, all at once, without any contradiction—or perhaps with every contradiction, which is one of the ways of Goddesses.
Perhaps no text shows us these Divine Feminine contradictions/not-contradictions as clearly as “The Thunder, Perfect Mind,” a text found among the Nag Hammadi texts. It is a long poem in the voice of a Feminine Divine Power that some scholars have linked to Isis; or at least that Her worship influenced the content of the text. Could be, but in my opinion, the Divine Speaker may be better understood as Sophia—with Whom Isis is also identified. The Coptic (late Egyptian) manuscript from which the text comes is dated to roughly 350 CE. Here’s a brief excerpt from this amazing work:
For I am the first and the last. I am the honored one and the scorned one. I am the whore and the holy one. I am the wife and the virgin. I am the mother and the daughter. I am the members of my mother. I am the barren one and many are her sons. I am she whose wedding is great, and I have not taken a husband.
The Thunder, Perfect MindClearly, Isis is identified with Virgin Goddesses throughout the Mediterranean world. And it is not at all unusual for such Goddesses to be both virginal and associated with fertility. What about Egyptian sources?
The ancient Egyptians were not quite so concerned with virgins—by which I mean, in this case, a young person who has not yet had sex—as were the Greeks and some other Mediterranean peoples. For instance, there was no requirement that young women, or young men for that matter, be sexually inexperienced when they married. Many young women probably were—particularly those who were married very young to older husbands. But prior to marriage, young people might engage relatively freely with each other. After marriage, sexual exclusivity with demanded, especially for women. The penalties for non-compliance could be very harsh, especially for women.
This is not to say that Egyptian virginity was not valued or even required under certain circumstances. The text that included the lamentation songs of Isis and Nephthys noted above specifies that the priestesses taking the roles of Isis and Nephthys be “pure of body and virgin” and also that they are to have their body hair removed, wigs on their heads, tambourines in their hands, and the names of Isis and Nephthys inscribed on their arms.
This text, one of very few we have, is from the Ptolemaic period, when Egypt had been influenced by Greek rule. I wonder whether virginity would have been considered necessary earlier. Perhaps the priestesses would have only had to abstain from sex for a period of time before their ritual service. We know that people serving in Egyptian temples had to abstain from sex for a time (at least a day, often a number of days) as part of their purification. But they weren’t virgins.
The God’s Wife of Amun, the highest of high priestesses and usually a female relation of the king, was virgin for life. Beginning in the 2nd Intermediate Period, the position of the God’s Wife gained a great deal of power, eventually becoming second only to the king. Interestingly, it was an “Isis”—Iset, the virgin daughter of Ramesses VI—who began the tradition of the God’s Wife being celibate. Later, in the Roman period, some Roman priestesses of Isis maintained lifelong virginity. And we know that the Roman Isiacs might maintain a 10-day period of pre-ritual chastity known as the Castimonium Isidis or Chastity of Isis.
Isis Herself is called the Great Virgin in one of the Egyptian hymns to Osiris (I believe it is from the Isis Chapel at Abydos; still checking into it.) In Egyptian, this would is Hunet Weret. Hunet is the word for girl or maiden, weret is the feminine form of great. Hunet is also the name for the pupil of the eye and is connected to the Hermetic treatise known as the Kore Kosmou, the “Virgin of the World.” You can read about those maidenly connections here. (And read about the Kore Kosmou here, here, and here. )Just like Greek parthenos, hunet could mean a virgin, a girl, a maiden, or just youthful. And all Egyptian Goddesses are forever young. A young boy or youth is hunu.
Parthenogenesis (asexual reproduction), was not unknown in Egypt, either. The First Creators in many Egyptian myths, such as the God Atum and the Goddess Neith, created everything from Themselves. Some Egyptian queens, such as Ahmose, Hatshepsut’s mother, were said to have given birth to pharaohs after sexual union with a God.
So, is Isis a Virgin Goddess? Yes. Does She have sex with Her Divine Husband? Yes. She is, as so many Goddesses are, Both And. She is a patroness of marital sexual desire and bliss and She is an ever-renewing, ever-youthful Virgin Goddess. On this holy day and every day, may She bless you with the gifts you most desire.