Do You Dream of Isis?
In this strange stay-home-and-stay-isolated world right now, many people are reporting changes in their dreaming patterns. More dreams, odd dreams, dreams that are not like their normal dreaming life. Are you dreaming more, dreaming weird? I know I am.
Our Lady is a Goddess of Dreams. People slept in Her temples, hoping for dreams of healing or divination. Interestingly, the most common Egyptian term for dream was rsw.t, from a root meaning “to awaken.” So in dream, we awaken in our sleep…
Does Isis communicate with you in your dreams?
In Egypt, as in most of the ancient world, people definitely paid attention to their dreams. Kings and commoners alike regularly acted on messages received in dream. Sometimes the dreams were clear, the message needing no interpretation. Or a dream might be prophetic, providing information or warnings about the future. Some dreams instructed the dreamer to carry out certain actions; the temples were full of dedicatory plaques to the Deities stating that some action was taken “in accordance with a dream.” Yet these types of dreams were rare—as they are today. Most often, people dreamed in symbols and images that had to be interpreted in order to understand the meaning. For this, one needed a dream interpreter.
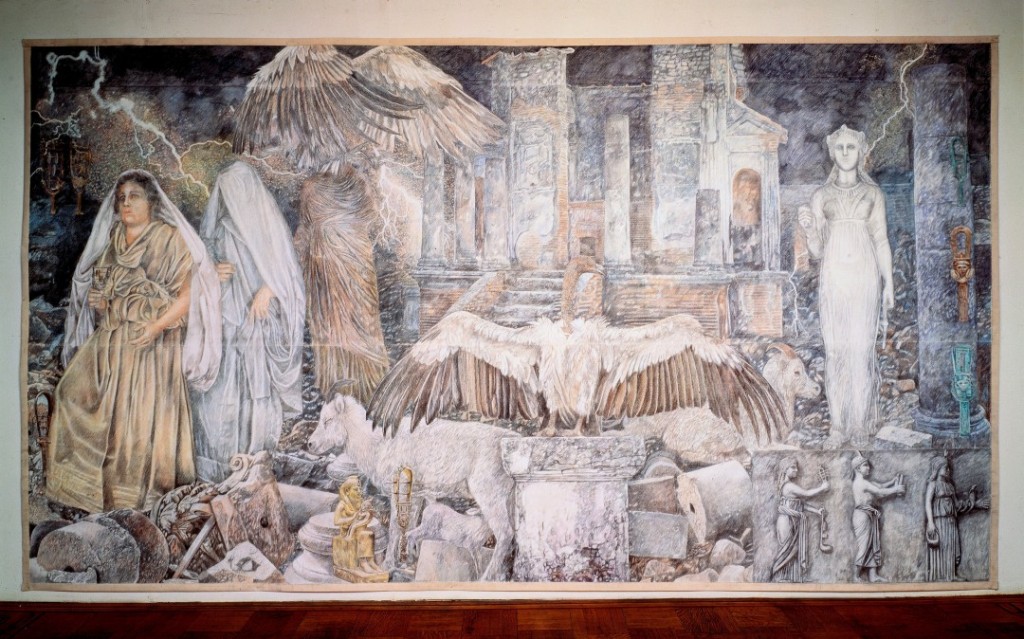

(The artwork above was inspired by a dream the artist had of the Temple of Isis in Pompeii. See what her dream was and more of her work here.)
The dream interpreter might be a village wise woman like the one of whom we have evidence from Deir el-Medina. Dream interpreters would set up shop outside the temples—especially during festival days. But most often the dream interpreter would have been one of the priests or priestesses of the Houses of Life at the great temples. Dream Books cataloged dream symbols and their meanings and may have served as resources for the temple interpreters. We have several surviving examples of these dream books.
In addition to bringing one’s dream to the temples for interpretation, one might also seek a special dream by sleeping in the temple. This sacred sleep is known to scholars using the Latin term incubatio (Greek enkoimesis) and was particularly associated with healing temples and healing Deities, such as Isis, Hathor, and Asclepius. It was a frequent practice in temples of Isis. In fact, the temples of Isis at Memphis and Canopus were quite famous for incubation. The Goddess was known to provide accurate diagnoses and effective prescriptions to those who appealed to Her. Diodorus Siculus records that She
gives assistance in their sleep to those seeking it, visibly revealing her very own presence and her beneficence towards those in need. As proof of these claims they say that they themselves offer not myths akin to those of the Greeks, but visible results: for nearly all of the inhabited world serves as witness for them, seeking to add to her honors because of her manifestation through healings. For appearing in their sleep she gives aid to the sick against their diseases, and those who heed her regain their health contrary to all expectation.
An example of an Isis incubation dream survives from a Greek orator named Aristides. Aristides spent a great deal of time visiting healing shrines due to his chronic illness. (Some have even called him a hypochondriac.) In one of his books, he describes a number of synchronicities surrounding a sacrifice of geese to Isis that was surely part of his pre-incubation rite. Then he gives a hint about his dream, writing that a light came from Isis relating to his salvation.
Another interesting example of incubation in an Isis temple comes from a letter written from Aspasia (470-410 BCE), the hetaira who was so beloved by the Athenian statesman Pericles, to Pericles telling him of her journey to several temples of healing to seek relief for (perhaps) a skin irritation of some kind. On the advice of her physician, she first visited the temple of Isis in Memphis. She writes, “I beheld the statue of Isis and her son Orus, seated on a throne supported by two lions” and says that sebestus (a species of Egyptian date) grew about Her shrine and describes the burning of incense in the morning, myrrh during the day, and cyplis [kyphi?] in the evening.”
Aspasia slept in the temple, but says she found no relief. The problem, according to the temple attendants, was Aspasia’s “incredulity.”
Next she went to the temple of Hygieia at Patras where the Goddess “appeared to me in the form of a mysterious pentagon.” Finally it was Aphrodite Who, in in the form of a dove, cured Aspasia.
I include this interesting anecdote for several reasons: first, to demonstrate that then, as now, the hoped for dream communication may not always come to us; second, that “mysterious pentagon” form in which Hygieia appeared to Aspasia. It is likely that the “mysterious pentagon” was the Pythagorean pentagram associated with Hygieia and used as a symbol of recognition among the Pythagoreans. As an educated woman, Aspasia conversed with philosophers, was a philosopher herself, even being described as “a female Socrates” by one ancient writer. And finally, Who better than Aphrodite to heal a hetaira? For me, Aspasia’s experiences ring true and reflect some of the many and varied ways the Deities can interact—or not—with us.
Isis is also known to call to Her initiates and devotees in dream. In Apuleius’ tale that culminates with his protagonist’s initiation into the Mysteries of Isis, we learn that Lucius must remain in the temple of the Goddess—waiting patiently—until he receives a summons from Isis Herself. Only then, when he knew for certain that Isis had invited him, could he undergo the ceremony of his initiation and further cultivate his relationship with the Goddess.
Dream invitation is part of modern devotion to Isis as well. Many are the modern priestesses and priests of Isis who were called to Her service in dream or in vision, which we may think of as a waking dream.
Yet, as always, there are cautions that go along with all this dreaming and visioning. We cannot forget that any information that comes from Her comes through us. The dream or vision-seed of information may come from Isis, but it passes through our human minds and souls, as well as our physical brains and bodies. It’s easy for that seed to be affected by what’s going on with us, in our daily lives and in our spiritual lives. There’s no way to avoid this. The best we can do is to try to develop wisdom and self-knowledge so that we don’t fool ourselves into thinking Isis told us something when we were really just hearing our internal echo chamber. Yet, as long as we can recognize it as our own stuff, this too can be a valuable learning experience.
If we can be honest with ourselves, then when we do have an important dream or vision, we will more easily be able to recognize it. The dream or vision will be more vivid—in our minds, hearts, and memories. We will have a sense of its importance and, at least for us, truth. (Never, ever rely on memory alone; write it down, please. I speak from experience.)
Once Isis has made Herself known to us in our dreams or visions, then it is up to us to take Her up on Her invitation or take up any tasks She may have given us.

Why Does Isis Have Wings?
Well, dang it. It appears our Oregon stay at home rules have been extended through September…which means no Isia Festival this year. It had been planned for this September. So we will just postpone a year and pick things up next time. Sigh. My many thanks to the over 20 people who so graciously and enthusiastically joined the Isia Crewe. We shall meet again next time!
______________________
THE most popular post on this blog is the one I’m reposting today: Why Does Isis Have Wings? Please read on for my answer, but I would love to hear about your experiences with Her wings in the comments. They are indeed magical and powerful.

So why DOES Isis have wings? Or perhaps it would be more accurate to ask why images of Isis have wings. As a Goddess, Isis takes whatever form She likes, of course. So the question is, what do the wings mean to us that makes them important in images of Her?
The first and easiest answer is that Isis is a Bird Goddess. Her most important sacred animal is a bird of prey. The Goddess often takes the form of Her sacred raptor; the kestrel (the most common falcon in Egypt) or the black kite.

In Egyptian art, when Isis and Nephthys are not shown as women, They are shown in full bird-form or sometimes as woman-headed kites or kestrels sitting or hovering by the bier of Osiris. As birds, Isis and Nephthys mourn Osiris, screeching Their shrill bird cries to express Their sorrow. Even quite late, Isis and Nephthys were shown with wings attached to Their arms—which is the way we are most used to seeing Isis’ wings portrayed—or wearing a garment of stylized wings that wrap gracefully around Their bodies.
Kites were connected with funeral customs from at least the beginning of the Old Kingdom, if not earlier. Texts speak of a woman called The Kite who was the Pharaoh’s chief female funerary attendant. She was supposed to remove poisons from the deceased, magically purifying him.

Soon there are two Kites—specifically identified as Isis and Nephthys in the Pyramid Texts. The Kites not only lamented and purified Osiris, but also were responsible for ferrying Him to the Otherworld. It is not until the New Kingdom that we find illustrations of Isis and Nephthys as kestrels.
Black kites are fairly large, dark-plumed birds that feed on both live prey and scavenge for carrion. They are sociable, intelligent, and aggressive birds—and would even attack wounded human beings. It may have been the bird’s fierceness that inspired one of the earliest Pharaohs to take the name Kite.
Isis is fierce in protecting Osiris. And both Sisters are fierce in Their lamentations for the God. The black kite’s cry—a shrill, plaintive, screeching—may have sounded to the ancient Egyptians like wailing, lamenting women. It may have been that the ancients saw a correspondence between the kite’s scavenging for carrion and Isis’s scavenging for the scattered pieces of Her husband Osiris’ body in order to assemble them for renewal. Or perhaps in the cleverness of the black kite the Egyptians saw a reflection of the cleverness of the Goddess Isis as She tricked the enemy Set time and again.

On a magical level, Isis’ wings are the means by which She fans renewed life into Osiris. They are the protection spread out over the deceased in the tomb. Their shadow is our shelter in this life and the next. For human beings, wings have always exerted a strong fascination and engendered intense longing. We are in awe of the ability of winged creatures to fly under their own power. Even today when flight is available through mechanical means, many, many people still have “the flying dream.” In the dream, we fly on our own, our arms held out to our sides like huge wings, soaring like great, wild birds. Yet beyond physical flight, wings also commonly symbolize spiritual flight—ascent to the Heavens. And since feelings of rising, floating, or flying upwards can accompany spiritual experience, it is quite natural for cultures throughout the world to conceive of spirit beings—from angels to faeries—as winged.
In Egypt, a very ancient conception of the cosmos envisioned the Heavens as the enormous wings of the great falcon God Horus. These heavenly wings, attached to the disk of the Sun, were a common Egyptian protective motif. In fact, the image of the winged disk of Egypt was so powerful that other peoples, such as the Babylonians and the Hittites, adopted it. Some scholars believe that the beautiful Hebrew biblical phrase “the sun of righteousness shall arise with healing in his wings” may have been inspired by the Egyptian symbol of the winged solar disk.

This protective aspect of the symbol of wings was key in Egyptian thought; so almost invariably, when you see the open wings of a Deity, the wings are intended to protect—and Isis is the protective Goddess par excellence.

Furthermore, the Egyptian word for “to fold the wings,” sekhen, also means to embrace. An Egyptian mourning posture mimicked the protective embrace of Osiris by Isis. And surely, it was Isis’ protecting, enfolding, winged arms that the Egyptian mother had in mind when she recited this protective charm for her child: “My arms are over this child—the arms of Isis are over him, as she put her arms over her son Horus.” Nevertheless, the wings of Isis could also be aggressive, one text tells us that Isis “struck with Her wing” and closed the mouth of a river.
The open wings of Isis can also be related to a posture seen in images of the ancient Egyptian Bird Goddess. This is the posture of the famous Neolithic statuette of a so-called dancing woman with her arms raised in an open curve above her head, and which has become a popular amulet among modern Goddess worshippers. The same posture can be seen in the Goddess figures that ride in the curved boats that were a favorite theme of pre-dynastic Egyptian pottery and petroglyphs.

According to Egyptologist Louis Breasted, the posture is typical of Egypt. And although these ancient figures do not have obvious wings, their unwinged but upraised arms foreshadow the winged, upraised arms of Goddesses seen in later Egyptian art. These beak-faced figures are often identified as Bird Goddesses, so perhaps the wings are implied—or they may indicate that the figures represent human priestesses who are imitating their Bird Goddess. Whatever the case, the “wing” stance is a posture of great antiquity and numenosity and many researchers consider it to be characteristic of the Divine Feminine. Read more about these ancient images here.
If you wish to experiment with the power of Isis’ wings for yourself, try The Wings & Breath of Isis on page 268 of the new edition of Isis Magic.
The Return of the Goddess * Wicca-Spirituality.com
The Return of the Goddess * Wicca-Spirituality.com
WHAT–If Anything–Could Ascension Mean to Wiccans? * Wicca-Spirituality
WHAT–If Anything–Could Ascension Mean to Wiccans? * Wicca-Spirituality
The Exaltation of the Queen of Heaven
The Exaltation of the Queen of Heaven
The Awe-full-ness of the Goddess
I recently came across a collection of epithets of Isis in which the author translated the core concept as “awful.” In the original sense of the word— “full of awe” —awful makes complete sense as a Divine epithet. In our common understanding of the word today, it’s…oh, let’s say…uncomfortable.

So you can get a full taste of the strangeness of it, here are some of Isis’ awful epithets: She is “The Lady of Awfulness,” “The Lady of Awfulness More than the Divine Powers,” “She Whose Awfulness is Great,” and “She Whose Awfulness is Greater than the Gods.” She is awful on earth, in the heavens, among the Deities, in Egypt. She is “Great of Trembling” and “Hundreds of Thousands Tremble at Her Sight.”
Oooh, scary.
And, She is. Scary. Sometimes.
So today, let’s talk about the awfulness of Isis.
The ancient Egyptian word translated as “awful” is transliterated nrw. To be able to pronounce it, we go with neru. It is associated with the vulture and with Isis and Nephthys as two Vulture Goddesses, the Nerti. (And you recall that the word for vulture in Egyptian is mut, that is, mother.) The ner root means to be strong, to be mighty, to terrify, to strike awe, to be victorious. Neru can be The Terrible One…or the concept of strength, might, or victory. It can also be fear or dread. Neri can be to over-awe. There is a Goddess of Strength called Nerit. And ner also can have connotations of protection because of the Awful One’s strength and might and power to protect. So, I guess, “awful” may be a pretty good translation of the idea.
Iset Nerit is Isis Who Strikes Awe.*

An awe-some Isis by Ugo Sirius. Find more of his work here.
If you are just beginning your relationship with Isis, it is likely that you haven’t met Iset Nerit yet. Most often, we first meet kindly Isis, the Great Mother, the protectress. Ah, but Nerit is always there. For instance, She may come to you disguised as Isis the Ass Kicker. Or She may give you a glimpse of Her fierceness or Her fire.

But it is when Isis is at Her Most Primordial, Most Ancient, Most—ENORMOUS—that is when we are truly greeting Iset Nerit. In Her presence, my belly thrills, my spine shivers, my hair stands on end. The numinous, the holy, the strange, and the powerful is with me, before me, around me. I kneel and kiss the ground before Her beautiful face.
For some, this experience may be somewhat unsettling. I am reminded of some folks of my acquaintance who apparently thought we were playing at magic, pretending about the Goddesses and Gods. Then magic actually happened and the Goddess was really there and they were done.
If you are in the early days of your relationship with Isis, I suggest that you not seek out Iset Nerit. Not yet. Unless, of course, you like the feeling of sacred fright before the Divine. Some of us do (she admits sheepishly).
What about you? Do you know the awe-full-ness of Isis?
*For Coptic fans, Nerit is Noure (noor-ray), which is rather beautiful in the same soft way that Coptic Ise (Ee-say) is: Ise Noure.
She Will Hear You
It has now been about a month that we’ve been under a stay-at-home directive here in Oregon. And it’s working. Even though the Pacific NW had the first case of Covid-19 in the US, total cases here put us in the lower half of affected states. May that continue to be the case.
But perhaps you are wondering, “where is Isis in all this?”

She is here.
As She has always been.
And She is listening.
In fact, Isis is one of the Deities particularly known to hear our human cries, to hear our prayers. She is called the One Who Listens. In ancient texts and on temple walls, Isis is She Who Hears Petitions; Who Hears the Petitions of Millions. She is particularly known to come at the invocation of Her devotees: Isis is She Who Comes to the Calling; people Call to Her in Every Place. A graffito from Thebes says, “O you of all lands, call to Isis, the Great Goddess, She listens at every moment!”

Why then does She not snap Her magical fingers and make it all go away? Because that’s not how it works. This is our problem to solve and we will solve it. But She reminds us that we are each a feather in Her Wings, the blood in Her veins, the extension of the magic in Her hands.
This is a time not to neglect our connection with Her. Meditate, make offerings, chant. She invites us to let our souls fly to Her and be enfolded in Her Wings. “Bring your heart to Me,” She says. “Speak pain. Speak truth.” She will take us as we are right now.
For She listens. And She hears.
Isis & Sakhmet or Isis-Sakhmet?

A friend was asking about Sakhmet today, and so here’s a little something about Isis and Sakhmet…
Many are the modern devotees who are attracted to Sakhmet, ancient Egypt’s fierce Lioness Goddess. Her name means The Powerful One, the Mighty One, or the Female Power. And She is powerful indeed.
Quite a few images of the Goddess remain to us, for hundreds of them were set up at the Temple of Mut at Karnak. The Vatican Museum has about a half dozen of these and has created a semi-circle of the bigger-than-human-sized Sakhmet images in an outdoor area that is part of the “profane” section of the museum. (Yes, of course, I headed straight to the profane section.) I have also been fortunate to have seen several of these beautiful statues here in Portland as part of traveling museum shows.
But it was a smaller image of Sakhmet in one of these shows that literally blew my astral hair back. All that was left was the head, about eight inches high. It was made of a yellow, semi-translucent stone and it quite simply hummed with magical power. After all these years. Still. Powerful. I was mesmerized. It’s probably a good thing the image was behind glass because I certainly would have touched it—and probably gotten tossed out on my tushie as I had already been tut-tutted at for almost touching one of the larger Sakhmets. Such is Her power.
If you’ve been following along, you’ll already have noted that Isis has Her fierce aspects, too. And in the typical fluid way of the ancient Egyptian Deities, Isis and Sakhmet can become One. One of the places where this is true is in the Isis temple at Philae where Isis and Sakhmet are specifically identified. Here’s one of the hymns to Isis from that temple, translated by Louis Zabkar:
Giver of Life, Lady of the Sacred Mound,
Lady and Mistress of Philae,
August and mighty one,
Lady of the southern lands;
Sakhmet, the fiery one, who destroys the enemies of her brother,
Those disaffected of heart, the enemies of Hor-ankhti;
Princess, Mistress of Upper and Lower Egypt,
Mighty one, foremost of the Goddesses;
Ruler in Heaven, queen on earth,
Sun-goddess in the circuit of the sun-disc;
Mistress of battle, Montu of combat,
One to whom one cries out on the day of encounter;
Mighty protectress without her equal,
Who saves all those she loves on the battlefield;
Whatever comes forth from her mouth is accomplished immediately,
All the gods are under her command;
Great of magic, when she is in the palace,
Great one upon whose command the king gloriously appears on the throne.
As we see here, Isis is specifically called Sakhmet, as well as being described as “mighty,” and “the mighty one,” the very meaning of Sakhmet’s name. You’ll also recall that in the Jumilhac papyrus, Isis is said to have transformed Herself “into Her mother Sakhmet.”
In this hymn, Isis appears as a strong battle leader, destroying enemies, protecting Her people and their king through Her powerful magic. For the Egyptians, this type of power was often expressed using fiery imagery. Thus, in the hymn above, Isis-Sakhmet is “the fiery one.” Elsewhere at Philae, Isis is called Lady of Flame. She is also the fiery Sun Goddess. And She is one of the fire-spitting Uraeus Goddesses Who sits on the brow of Re as one of His Eyes. As the Eye of Re, She is the fiery Power That Goes Forth and “slays Apophis in an instant,” according to another Philae hymn.
At Her great temple at Philae, we see many sides of the Great Goddess Isis. She is at once the beautiful Cow Mother, watering the sarcophagus of Osiris so that new life sprouts from His dead body, and the fierce-faced Isis-Sakhmet, Isis the Powerful One, the Great Female Power. May Her strength always protect you.
The Lamentations of Isis
One of the rituals that will be part of our local (Pacific NW) 2020 Fall Equinox Isia Festival is the “Lamentations of Isis.”

This rite is an adaptation of the lamentations ritual in Isis Magic.
Our festival version is non-gendered and changes have been made to allow for a larger group of participants.
If you think that you’d like to be a part of this rite, please read on so you’ll know how to prepare. For additional reading, here’s a post about Isis and lamentation.
About the Rite: Lamentation has always been a part of the honoring of Isis. We even have some of the actual scripts of the laments for Osiris that were performed in the temples, though all the surviving records date from the later Ptolemaic period. They are evocative and, in some cases, quite heartbreaking. In Imperial Rome, where Isis became enormously popular, the Isis religion was notorious for its large, highly emotional, public enactments of the lamentations of the Goddess. The cathartic value of this emotional release was one of the attractive features of the religion for worshippers who found the Roman state religion too sterile.

I have not felt the need for this rite for many years. But that has changed. And I have the feeling that I am not alone. If you would like to not be alone in your own laments, please join us for this afternoon ritual. Know that if you participate in this rite, you may face your innermost pain. Be sure that you are ready and that your heart fully consents to this Work.
This rite of lamentation allows for an emotional release that is intended to ease the pain in our souls, freeing us from that pain so that we are able, once again, to take action. During the course of the rite, we lament societal, personal, and spiritual wounds, each followed by a cleansing with water to make the catharsis tangible.

The “Lamentations of Isis” are just one part of the greater Isia Festival. This rite takes place on Friday afternoon, giving us time to lament, but also giving us time to move into a place of rebirth and renewal through the other rites and activities of The Isia.
Ritual Preparation: Sometime before you arrive at the Festival, take time to read or remember the myth of Isis and Osiris. Attempt to identify with the sufferings of Isis as She endures the murder of Her Beloved and searches for His dismembered body. Let your own sufferings rise in your mind in response to reading about the sufferings of Isis. Feel them, but do not try to analyze them to any extent.

Please arrive for the rite wearing blue or white, the colors often worn by Egyptian mourners, or come in black, the Hellenistic color of mourning and a color also worn often here in the US. Black robes came to be particularly associated with Isis as Her religion spread throughout the Greco-Roman world; She was called Melanophoros, the “Wearer of the Black,” and in at least one place, Her devotees were also called Melanophoroi. (You may wear a full-length robe or simply blue, white, or black clothing, as you see fit.) You should also bind your hair tightly to your head. If you have short hair or no hair, bind your head with cloth or scarves, turban-style. The point is to arrive at the ritual with a feeling of tightness about your head. We will be unbinding ourselves as part of the rite.

In addition, bring with you a chalice and a black Isis band (a blindfold; i.e. a strip of black cloth; it would be ideal to bless this cloth in the name of Isis before you come). Finally, also bring a white votive candle or tealight in a container.
The lamentations are guided by nine ritualists. There are three Priestesses or Priests of the Circle, who facilitate the first lament, three Priest/esses of the Triangle, who facilitate the second lament, and three Priest/esses of the Point, who facilitate the third lament. In addition to other ritual responsibilities, the Priest/esses of the Circle 3, Triangle 3, and Point 3 lead the purifications with water and the Priest/ess of the Point 1 will take on the kheper or Goddessform of Isis for the resolution of the third lament.
If you have questions about this ritual, please feel free to leave them in the comments and I’ll do my best to answer. May She keep you well and Under Her Wings, as always.

Easter and the Coming of Spring
 Happy Easter, everybody! Mother and Daughter are reunited and the spring is here.
The world is renewed in springtime and the egg has for long ages been associated with this time. Ancient cultures including the Chinese, the Egyptians and the Romans decorated eggs to celebrate the coming of spring.
Read about the High Feast of Easter and about the origin of the Easter Egg.
Happy Easter, everybody! Mother and Daughter are reunited and the spring is here.
The world is renewed in springtime and the egg has for long ages been associated with this time. Ancient cultures including the Chinese, the Egyptians and the Romans decorated eggs to celebrate the coming of spring.
Read about the High Feast of Easter and about the origin of the Easter Egg. Easter and the Coming of Spring
 Happy Easter, everybody! Mother and Daughter are reunited and the spring is here.
The world is renewed in springtime and the egg has for long ages been associated with this time. Ancient cultures including the Chinese, the Egyptians and the Romans decorated eggs to celebrate the coming of spring.
Read about the High Feast of Easter and about the origin of the Easter Egg.
Happy Easter, everybody! Mother and Daughter are reunited and the spring is here.
The world is renewed in springtime and the egg has for long ages been associated with this time. Ancient cultures including the Chinese, the Egyptians and the Romans decorated eggs to celebrate the coming of spring.
Read about the High Feast of Easter and about the origin of the Easter Egg. Are You there, Isis? It’s me, Isidora.
In these days of “self-isolating,” are you perhaps feeling a bit disconnected; not only from others, but from Her?

It’s pretty weird out there right now, folks. For one thing, I’m in Portland Oregon and it’s snowing. In mid-March. Politics? Don’t get me started. Oh, and then there’s the fact that every grocery store in town is out of just about everything because people are preparing to be “self-isolating” at home for a good long while. Of course, it’s not that we shouldn’t be taking this pandemic seriously. We should. And we are.
But all the crazy out there can make us feel a little, well, crazy. Which is not very conducive to experiencing our connection with Isis. It might even make us panic. Is She still there? Was She ever there? Am I “losing my faith”? What’s wrong with me? What’s wrong with Her?
If you’ve been missing Isis (or perhaps She’s been missing you?) there are things you can do about it. Without adding to your crazy.
First, give yourself a break. Have you been trying too hard, pushing too much? While having a daily practice is wonderful, if you’re doing the same thing every day, that once-lovely little ritual can become routine, even boring. Consider taking a break. If you do a daily rite, cut back to once a week. Or try a different ritual. It could be that a rite that hadn’t caught your attention before would be just right now.

On the other hand (hey, these aren’t one-size-fits-all suggestions), a boring ritual might be just what you need. If you haven’t been doing ritual, pick one and do it. At least once a week. Pour a libation. Offer flowers. Perform the “Lotus Wand of Isis” or the “Opening of the Ways” (both in Isis Magic). Oh, and don’t expect any spiritual fireworks. You might get them. Or you might not. Either way, it’s okay.
Take a trip down memory lane. Think back on what first got you excited about Isis. What was that like for you? Reminisce. Perhaps there was a particular book that inspired you? Re-read it. Was there an experience you could recreate?
Give yourself a magical task. You can define this any way you wish. You might try something like this: every time you pass through a doorway/see a hawk/wake up in the morning, say to yourself, “Isis is all things, and all things are Isis” or “I open myself to Isis” or whatever seems right to you. By thinking of Her and speaking Her name, you will reweave your connection with Her.

Don’t feel guilty about it. This happens to every person who has ever been on a spiritual journey. If it has never happened to you before, you’ve beaten the odds. But it has now, and chances are, it will happen again. And that’s okay, too. That’s why we have to be kind to ourselves during these times of spiritual emptiness. We haven’t failed because we have doubts or have fallen away from awareness or practice. We’re just a normal human person and this is just part of the path. And She will be waiting there for us when we’re ready.
Nevertheless, persist. Always take the next step on that path. Sometimes a spiritual project is a great way to reconnect with Isis. If you’re solitary, you might create an artwork for Her/of Her. Write an invocation. Choreograph a dance. Cook an Isis feast and invite Pagan friendlies to join you in eating it and honoring Her. Are you a ritualist? Create a new rite for Her. If you’re fortunate enough to have a community, gather some fellow Isiacs and come up with something together.
Pick any one of these things to try. You’ll see. Oh. And now the sun’s out here in Portland. The snow is melting. And spring is coming.

Join Us for the Isia Festival, Fall Equinox, 2020

Well. We have a date, so that’s official.
We have a dozen incredible ritualists—so far—so that’s official.
I shall begin losing my mind any minute now, so that’s decidedly official.
What am I talking about? The Pacific NW Fall Equinox Festival at Ffynnon, Oregon.
If you are within reasonable distance of the area, do mark your calendars for Sept. 17-20, 2020. We will be celebrating the Festival of the Isia, a festival of the Lamentations of Isis and the Renewal of Osiris Beneath Her Wings. (And the renewal of all of us as well. I know I could use a little renewal right now. And more so as we get closer to November. You, too?)
If you are in the Portland area and would like to help, get in touch with me. Comment here, message on FB, or email me if you already have my address.

Fall equinox is (roughly) the time of the ancient festival of Khoiak, from Egyptian ka-her-ka, “sustenance upon sustenance.” It is one of the best-attested ancient Egyptian festivals. The festival revolved around the most well-known of the myths of Isis and Osiris: the story of His death, Her mourning, and Her resurrection of Him—along with the resurrection of the grain that would be the next year’s food stores, hence “sustenance.”
The 2020 Isia Festival will be our version of these ancient rites.
We will participate in the Lamentations of Isis—and have the opportunity to make our own personal laments. We will join the Goddesses and Gods in the Search for Osiris. We will participate in the Raising of Osiris and, with Him, be renewed Under Her Wings. Each day we will open Her shrine with beautiful rites, each night we will close it. There will will be meditations, offerings, and workshops throughout the festival that we can all take part in.
This blog started 10 years ago when we celebrated the Radiant Isis festival. I am so pleased to be able to celebrate another community-wide festival for Her this year. I hope you will join me Under Her Wings.

Perfumes for Isis
At this present moment, our home is filled with flowers. Yes, I know. It’s February. That’s why it’s filled with flowers. And since oriental lilies are some of our favorites, right now, I’m smelling the sweet-dark scent of those wonderful lilies throughout the living room.
And all this leads me to think of the perfumes of ancient Egypt and, of course, the perfumes of Isis particularly. For the Goddesses and Gods of Egypt were always associated with scent. Beautiful scents have always been connected with the Divine, but in Egypt particularly, you knew that a Deity had arrived when you smelled Her or His perfume in the temple air.
The Egyptians apparently blended scents appropriate for their Deities; for instance, there is a record of an unguent called “Aroma of Horus.” Surely, there was an “Aroma of Isis,” too, but alas, we have no record of it to date. Today’s magical perfumers, on the other hand, almost always have a scent for Her. Isis’ association with scent remained part of Her manifestation even after Her worship spread beyond Egypt. In Apuleius’ account of initiation into the Mysteries of Isis, his protagonist sees Isis in a vision and remarks that She breathed forth the “blessed fragrance of Arabia.”
My personal favorite scent for Isis is stargazer lily. With its deep pink, engorged-looking blossoms, stargazers are downright sexual in their showiness. Of course that is exactly what any flower is; sexual. As you may know, flowers are the sex organs of plants, which they display for all the world to see, marvel at, and enjoy. No wonder we have always given flowers as a love gift.
I like the blatant, vulva-pink sexual display of the stargazer to be sure. And the flower’s name reminds me of Isis’ own starry connections. But the main reason I associate them with Isis, and give them in offering to Her, is the scent. The stargazer’s soft, sweet perfume is deepened with a dark, funky musk that is almost animal-like in its pungency. The stargazer is my “jitterbug perfume.” (If you have not read Tom Robbin’s Jitterbug Perfume, oh please do!) The mixture of sweet and strange all wrapped up in an audacious package seems to me a perfect floral resumé for Isis. She offers us the sweet love of a mother one moment, then freaks us out completely with some weirdly magical happening the next. Like the flower, She is not shy; never shy. She will always tell you what you need to hear even when you don’t particularly want to hear it. Thus do I offer unto Isis that which is Hers: the beautiful stargazer lily.
The ancient Egyptians had no stargazers, alas. But they did associate a variety of other scents with Isis as well as with other Deities.
Expeditions to Punt for cinnamon, frankincense, myrrh, and other precious resins, were common throughout Egyptian history. The huge gardens attached to the temple complexes also supplied vast quantities of herbs and flowers for the creation of the gallons of scent, pounds of incense, and thousands of bouquets offered in Egyptian temples. Many temples, such as those at Edfu and Denderah, even had special laboratories for making perfume and incense. Perfume was, after all, one of Egypt’s most lucrative exports.
Cleopatra VII, the queen who styled herself “the New Isis,” was reputed to use a different perfume for every part of her body and was credited with writing a book on the subject. But Cleo’s perfumes would not have been the clear, alcohol-based liquids we think of as perfume today. Egyptian perfumes were oil and fat-based; similar to our solid perfumes that liquefy as they are rubbed into the skin. A number of Egyptian perfumes were quite famous, the name brands of their day.
Lily was the dominant scent in Susinon, a perfume that seems to have been made exclusively by women. Perhaps this was because the lily was connected with female sensuality and spirituality and lily oil was a common treatment for “female complaints.” Lotus oil, from the sacred blue lotus (actually a blue water lily), was a favorite essential oil and associated with rebirth. It was the fragrance most favored by Egyptian priestesses. Other Egyptian perfumes include Magaleion, a complicated, difficult-to-make scent; Mendesian, known simply as “The Egyptian,” which was a spicy, resinous perfume; Metopion, a mixture of resins, herbs, sweet wine, and honey; and Sampsuchum, a marjoram-based scent sweetened with herbs and nasturtium flowers.
And then there was Kyphi, both an incense and perfume.
Recipes for Kyphi perfume are engraved on the walls of the temple of Isis’ son, Horus, at Edfu and at Philae, Isis’ own great temple in Upper Egypt. Kyphi was used especially to welcome the Deities to Their temples. Wine-based, Kyphi also includes sweet flag, rushes, cinnamon, juniper, raisins, myrrh, frankincense, cardamom, and gum mastic. In his essay “On Isis and Osiris,” Plutarch reports 16 ingredients and says that Kyphi calms, soothes, and can lull to sleep. It is also said to sharpen the intuition and promote dreams.
A priestess friend and I once made a ridiculously huge batch of Kyphi from Plutarch’s recipe, bits of which I am still burning to this day. It has a warm smell; like spicy raisin cookies. In fact, you could eat it without harm—and I believe the Egyptians did, medicinally. Luckily for me, it seems to get better with age.
What scents do you associate with Isis? There are no wrong answers. This is a personal thing. I’d love to hear your thoughts in the comments.
Goddess in the present tense…dammit

I do not often rant on this blog, as those of you who have been reading along well know. But you are about to read one. Okay, a tiny one. Sorry. Every now and then, this little rant gets kicked off by reading other writers…people who actually DO have a relationship with their Deities and who yet often do not use the present tense when speaking or writing about their Deities. So now you see where this is going…
If you’ve read Isis Magic or Offering to Isis, you may have noticed that—except when something actually is in the past—I always refer to the Goddess in present tense. In fact, I have been very, very, very, very conscious of doing so.
Because, you see, She IS.
She’s is not a Being Who was but is no more. She is not “just a myth,” some silly old story deserving of the past tense. Indeed, She is All that Is, and Was, and Ever Shall Be. She existed then, She exists now, and She will exist when the rugged, snowcapped mountain that, on a clear day, I can see from my rooftop has become a gentle, green hill.
And I know you know that. Which is why I am so puzzled when I sometimes see modern Pagans, Polytheists, Wiccans, Witches, and insert-your-self-definition-of-choice-here using the past tense about their Deities. The most recent one I saw, and which kicked off this rant, was a witch writing that “Hekate was…”
It happens most often when telling Their sacred stories, trying to offer a brief “definition” (as if that could be done!) of the Deity, or describing Their relationships with other Deities: “Isis was the Goddess of Magic.” Osiris was the husband of Isis.” Isn’t She still the Goddess of Magic? Isn’t He still Her husband? Now if you said, “To the ancient Egyptians, Isis was the Goddess of Magic and Osiris was Her husband,” that would work. No more ancient Egyptians around today, so what they considered is indeed history. To me, however, Isis IS the Goddess of Magic and Osiris IS Her beloved husband.
In writing of the history of the Isis religion and the many aspects in which She has appeared to humanity, I have always kept in mind that, to the people who worshipped Her then, as well as to those of us who do so today, Isis was and is a Living Goddess. She is not a historical curiosity. She is not a metaphor for our times. She is not feminist wish fulfillment. She is not merely a psychological archetype. She is Divine Love, Life, Magic, Mystery. She is Goddess and She is.
— Isis Magic
And speaking of myths, a myth isn’t something that is false— “oh, that’s just a myth.” No. A myth is a sacred story meant to tell us something about the Deity or Deities of the myth. Myths are “things that never happened but always are,” in the words of the 4th century CE Roman writer Sallustius. Or maybe myths are things that never happened historically, but are eternally true. Ask Joseph Campbell. Or Jean Huston. Or the many others who are doing Work with myths. And remember, just because it belongs to the corpus of the dominant monotheisms doesn’t mean it’s not mythology. Egyptian mythology is. Christian mythology is. Jewish mythology is. They are all sacred stories and they are all mythology.
Most of this, I think, comes from early and ongoing conditioning. Except for those of you young enough to have been born of Pagan parents, most of us were taught in school, from early on, that the ancient Deities were and mythology was. But let’s get over that. May we all just mind our tenses and our mythologies, please?

The Is-ness of Isis
But how do we know that Isis is? How do we know that She’s “real”? Must we simply “have faith”? Do we just choose to “believe in” Her? Can we prove Her is-ness?
We can prove Isis’ is-ness, Her reality, exactly as much as any human being can prove the reality of any Deity, which is to say, we cannot. There is no scientific proof for the Divine. There is no infallible book or teacher that holds all the answers to all the questions. Yet this—happily—means exactly nothing when it comes to the truth of Isis’ existence.
This question of belief and faith is much more vexed for those of us in non-mainstream (O how I dislike that designation!) religions. How often have you been asked by some friend or family member or (hopefully) well-meaning stranger, “Well, then, what do Isians—or Pagans or Polytheists or Wiccans or Witches or insert-your-self-definition-of-choice-here—believe?”
And how have you answered?
Many of us involved in alternative spirituality today were reared in one monotheistic religion or the other, most often, Christianity. From early on, we were taught to “believe in” God and Jesus. We were told that a particular book was the Word of God, “proved” that God was real, and explained precisely what He wanted us to do with our lives. In terms of religion, the clergy were to be our role models, the ones whose faith was strong, whose belief was true; we should have faith and believe as they do.
We got used to using those words, faith and belief, when speaking about religion. But perhaps those are not the right words.
For me, what proves that Isis is real is my experience of Her, not my faith or belief in Her. No single book is the touchstone for my spirituality, though I find spiritual truths in many, many books written by many, many wise human beings. I can’t transfer my deep knowing of Her reality to anyone else (though I admit that the exercises and rituals I share with others are attempts to at least set up the conditions that will enable others to discover their own experiences of Her). Nevertheless, experience of the Divine is an individual thing; each one of us must experience Isis for ourselves—even if we do so in a group. Clergy can facilitate. Books can show us a way. The experiences of others can strengthen us in our desire for our own experience of the Goddess. But, in the end, we will not truly know Isis for ourselves until we have our own experience of Her.
When that experience comes for the first time, it may bring awe, tears, joy, pain. When it comes again and again, throughout the many years, I can tell you that it may still bring all those things. But repeated and ongoing experience of the Goddess will also bring a true knowing, a personal gnosis, of Her. No longer operating just “on faith,” now we know Her reality because we have experienced it. No longer just believing, we have discovered Her truth for ourselves and it has become our truth.
The Sistrum of Isis
Hello, Isiacs! I’d like to share with you a beautiful double sistrum that one of our sisters discovered in a market in Baja. It is lovely and I’ll bet it sounds wonderful. Here’s the pic:

Why didn’t I think of that? A double sistrum! Thank you, Agnes. Here’s a repeat post about the sistrum and how this magical musical instrument can shake things up.
In Isis Magic, one of the key elemental implements of the priestess of Isis is the sistrum. It is one of several types of ancient Egyptian rattles that were used in the worship of the Goddesses and Gods. But it isn’t simply a musical instrument; it is also a magical instrument.
As you may already suspect, sistrum is a Latin word. In turn, it derives from a Greek term for the Egyptian rattle: seistron “that which is shaken.” The Egyptian terms are a bit more interesting. One of them is onomatopoeic, that is, the word sounds like the thing it represents. That one is sesheshet (say it out loud and you’ll see what I mean). The other is sekhem. And that one is quite interesting, for it means “power,” as in the name of the Goddess Sekhmet, the Powerful One. It is, of course, among the names of Isis as well.

The sistrum is an instrument of power. Even better, the term for “to play the sistrum” also derives from the sekhem root, so when you’re playing the sistrum, you’re “doing power.” That’s why the sistrum is the elemental Fire implement of the priestess or priest in the House of Isis.
Plutarch seems to be echoing the true Egyptian tradition when he explains in his essay “On Isis & Osiris”:
The sistrum also makes it clear that all things in existence need to be shaken, or rattled about, and never to cease from motion but, as it were, to be waked up and agitated when they grow drowsy and torpid. They say that they avert and repel Typhon by means of the sistrums, indicating thereby that when destruction constricts and checks Nature, generation releases and arouses it by means of motion. (Plutarch, Moralia, Book 5, “On Isis & Osiris,” section 63)
The vibration of the rattling sistrum is as the constant vibration of the atoms that make up all things and the activity of all living things.
Like many modern priestesses and priests of Isis, I have a collection of sistra (which is the plural of sistrum), including both handmade and purchased versions. Since the Coptic and Ethiopian Christian churches today still use sistra, you can actually purchase sistra that flow from the ancient Egyptian religious tradition. Naturally, I wanted to add one to my collection. So I ordered an inexpensive one online and when it came, it was, as expected, not super-high quality, but kinda sweet…except for the fact that the handle appeared to have been made out of ammunition casing. Eeewww. But the rattle sounded wonderful, nice and tinkly. I purified the sistrum and began using it.
Now here’s the part I like. Not too long after that—with no hard use of any kind—I picked up the sistrum one day to discover that the bullet-casing handle had split near where it was joined to the head of the sistrum. While I was disappointed that my new sistrum had broken, I was also somewhat relieved. Happily, I know artists—and an artist friend replaced the handle for me with copper tubing. My repristinated copper and brass Coptic sistrum has been rattling up power for Isis ever since.
In ancient Egypt, while the sistrum was used in the musical worship of all Egyptian Deities, it was especially associated with the worship of the Great Goddesses Hathor, Bast, and Isis. Generally, more priestesses than priests played the sistrum. Yet the archetypal sistrum player is Hathor’s son, Ihy, often called simply the Sistrum Player.
The creation of the sistrum is said to have developed from the polite habit of rattling the papyrus stalks before entering into the papyrus marshes. The marshes, you see, were often the dwelling places of fierce Wild Cow Goddesses, such as Hathor, and poisonous Cobra Goddesses, such as Wadjet. It was considered the wiser course of action to let Them know you were coming. (Never sneak up on a Goddess; all the myths tell us so.)
If we think of it as a polite knock on the door before coming into the presence of the Goddess, we can consider the rattling of the sistrum as an Opening of the Ways from the mundane to the sacred. It can also be used to stir up energy, in ourselves or our temple space, as well as to add emphasis and power to certain parts of a ritual. Softer rattling can be used meditatively and to bring down and sustain energy as the ancients did when they used it to “pacify” an angry Deity.
The sistrum became inextricably tied to Isis when Her worship spread into Greece and Rome. In fact, it was so commonly associated with Her in Rome that when ancient Romans saw a sistrum, they immediately thought of Isis and no one else. Even as late as the 4th century CE, Maurus Servius Honoratus, a grammarian with the contemporary reputation of being the most learned man of his generation, noted that
Isis is the genius [the spirit] of the Nile, who by the movement of her sistrum, which she carries in her right hand, signifies the access and recess [that is, the rising and falling] of the Nile… (Servius, Observations on the Aeneid, 1.8)
There were two types of ancient sistra, which we know as the naos sistrum and the hoop sistrum. In a naos sistrum, the top of the rattle is shaped like a small shrine (naos in Greek); in a hoop sistrum, the top is an elongated hoop. Holes were made in the sides of the naos or hoop and metal rods were inserted horizontally so that when the sistrum was shaken, the rods rattled in the holes. Sometimes additional pieces of metal were pierced and strung on the rods to amplify the sound. (Many modern sistra have this feature.)
If you’d like to Do Power for Isis, you may purchase a variety of ready made sistra. DeTraci Regula’s Isiscraft Catalog offers a number of lovely ones. You can find versions of sistra in music stores that specialize in ethic instruments. You can also order the Coptic ones online (but they will probably come with the bullet-casing handles). And, of course, you can also make your own.
An Isis devotee of my acquaintance made some wonderful small sistra by splitting a piece of bamboo (about 1/4 inch in diameter) 2/3 of the way down. She glued ribbon around the un-split part to keep the sistrum from splitting all the way and to create a handle. Then she glued a small piece of wood between the split bamboo as a wedge to hold the two sides apart, forming a “Y.”
Finally, she strung flattened and pierced bottle caps on wire and attached the wire to both sides of the split bamboo. While I have sistra in my collection on which I’ve spent quite a bit of money, these homemade ones remain some of my favorites.
If you have made your own sistrum, I’d love to hear about it.
Luciad: The Feast of Lights
 The Feast of Lights, also known as Luciad, is the first festival of the Easter cycle. It is a custom on this day for the coming year's candles to be blessed. Candlelight is symbolic of the gentle light of the Daughter that lightens the darkness of the world.
Read more about "Luciad: The Feast of Lights"
The Feast of Lights, also known as Luciad, is the first festival of the Easter cycle. It is a custom on this day for the coming year's candles to be blessed. Candlelight is symbolic of the gentle light of the Daughter that lightens the darkness of the world.
Read more about "Luciad: The Feast of Lights" Luciad: The Feast of Lights
 The Feast of Lights, also known as Luciad, is the first festival of the Easter cycle. It is a custom on this day for the coming year's candles to be blessed. Candlelight is symbolic of the gentle light of the Daughter that lightens the darkness of the world.
Read more about "Luciad: The Feast of Lights"
The Feast of Lights, also known as Luciad, is the first festival of the Easter cycle. It is a custom on this day for the coming year's candles to be blessed. Candlelight is symbolic of the gentle light of the Daughter that lightens the darkness of the world.
Read more about "Luciad: The Feast of Lights" I am Isis—the Goddess & Her Aretalogies
I very much like this Cosmic Isis by artist Dahlia Khodur. Here’s a link to her FB page.
Let’s talk a bit about the Isis aretalogies.
The aretalogies are those first-person statements in which the Goddess details Her many accomplishments and gifts to humankind. Here’s an except from one in case you need a little reminder:
I am She that riseth in the Dog Star.
I am She that is called Goddess by women.
For me was the city of Bubastis built.
I divided the earth from the heaven.
I showed the paths of the stars.I ordered the course of the sun and the moon.
I devised business in the sea.
I made strong the right.
I brought together woman and man.I appointed to women to bring their infants to birth in the tenth month.
I ordained that parents should be loved by children.
I laid punishment on those disposed without natural affection toward their parents.
I made with My brother Osiris an end to the eating of men.
I revealed mysteries unto men.
The word “aretalogy” is, as you may be able to tell, Greek. Arete means “virtues” and logy is from logos, “word,” so aretalogy is “speaking about virtues.” In aretalogy, the Deity is usually speaking in the first person about Her or His own virtues. But that’s not always so. For instance, the Aretalogy of Maronea is not spoken by the Goddess Herself, but by someone whom She healed. In Her honor, he speaks of Her virtues.
Isis is one of the few Deities for Whom we have quite a number of aretalogies. As with many Things Scholarly, there are disagreements about which of these documents should be considered aretalogies, so there’s no canonical count. But we can think in terms of six to ten. (That does not count the many, many hymns to the Goddess.)
The existing copies of these important documents are all written in Greek and date (we think) from the 2nd century BCE to the 2nd or 3rd century CE. Some of the scholars who have studied them have looked for ancient Egyptian precedents for the ideas in them, others believe them to be purely Greek in origin. Dieter Muller, a German Egyptologist who studied the texts extensively, took 56 phrases that refer to Isis in the aretalogies and tried to trace them to their sources. He concluded that nine were, in both form and content, Egyptian in origin, seven were Egyptian but expressed in a Greek way, 24 were of Greek origin, and 16 uncertain, but possibly Greek.
Another scholar, Jan Bergman, traced each of the statements to an original Egyptian concept claiming that the statements cannot be properly understood unless placed in context with Memphite religion and the relationship between the Egyptian Deities and Egyptian royalty. Louis Zabkar, an Italian-born Egyptologist who studied the hymns to Isis at Her Philae temple, believes that the Philae hymns contributed to the content of the aretalogies. In a epilog to his book about Isis’ Philae hymns, Zabkar takes another look at Muller’s work and expands the number of Egyptian-original aretalogical statements to 23, making them almost equal to the number of Greek-original statements. More recent scholars, too, have traced more and more of the self-statements to Egyptian originals.

Two of the aretalogies (from Kyme & Andros) state that they were copied from a stele “before the temple of Hephaestus [that is, Ptah] at Memphis.” Scholars thus sometimes refer to this as the M-text and believe that it could be the original from which all the other aretalogies were either copied or developed.
Some researchers have suggested that the thoughts of a famous Greek atheist contributed to the content of the Isis aretalogies. His name was Prodicus and he was a Greek philosopher (5th century BCE). His idea was that the gods were not divine at all, but were instead brilliant human beings from a primordial time who were so beneficial to humankind that people deified them. We usually hear of this idea tied to the name of a Greek mythographer named Euhemerus (4th century BCE). In fact, we even give it his name: euhemerism. But Euhemerus most likely got the idea from Prodicus.
Euhemerism was one of the ways the ancient Pagan Deities survived in the Christianized West. Since They (or they) were merely human beings, their myths could be retold—and even be used to teach “Christian” virtues. This definitely happened with Isis. (Isis Magic details some of the ways the story of Isis remained a part of the culture during this time.)
But what does all that have to do with the aretalogies? Some scholars (Fritz Graf; Albert Henrichs) suggest that this type of Prodican euhemerism—especially in relation to the cultural gifts of the Deities—was going on in the Eleusinian cults at that time. And, since Isis and Demeter were being equated, the Eleusinian euhemerism was applied to Isis and shows up in the Isis aretalogies. You can see it strongly in the Maronea aretalogy, which may be the oldest of these Isiac documents that we have. (It does not, however, explain the “I-am” structure of the Kyme aretalogy, which is very unlike Greek hymns and, in fact, has exact precedent in Egyptian sacred texts.)
Now, it’s not that the Eleusinians who took up some of Prodicus’ ideas were atheists themselves. We could say that they were merely adopting one of the memes of their day. They liked the idea of their Deity being the source of important aspects of culture and incorporated it.
Some scholars believe the Isis aretalogies were created as propaganda to help spread the gospel of Isis throughout the Mediterranean. At least to some extent, that’s probably so. But there are other ideas, too. I’m reading an article right now that argues they were read aloud as part of initiation into the Mysteries of Isis. To me, the argument isn’t persuasive due to the strict secrecy of the Mysteries. If the aretalogy was recited as part of the key epiphany of the Goddess in Her Mysteries, it would likely have been kept secret rather than carved in stone and set up before the temple of Ptah in Memphis. But it’s an intriguing idea nonetheless.
Interestingly, we have a dedication from the island of Delos made to Isis and Anubis by an “aretalogos.” If there was a regular priestly function as a Speaker of Aretalogies, perhaps the recitation of an aretalogy was part of the standard worship of the Goddess rather than part of Her Mysteries. Another suggestion is that they were read during Her great feasts.
Whether PR or liturgy, it seems most likely that both Egyptian and Greek elements formed the conceptual basis of the Isis aretalogies. Memphis was one of the places where Egyptian and Greek ideas came together, apparently without rancor. Here, key religious ideas of both Egyptians and Greeks blended, and could have resulted in the M-text.
But I wonder whether personal elements could have figured into the creation of the aretalogies as well. At least some of you have had Her speak to you in this way, telling you of Her arete in first person. It is a powerful experience; not likely to be forgotten. Perhaps you’ve even written it down to commemorate it. Who is to say that our ancient predecessors didn’t do the same?
For—as She has always done—Isis can speak directly to our hearts, telling us Who She Is, and especially Who She Is for us right now.
The Light of Isis
 As the days grow longer, a certain soft joy fills me.
As the days grow longer, a certain soft joy fills me.
By no means has winter here in my part of the Pacific Northwest been harsh. Yet I find that the increasing light releases me, urging me to draw in deep breaths that I didn’t even know I longed for.
That is what Light can do.
Many of us have spent so much of our spiritual capital in “accepting our inner darknesses,” that we can forget to take the time to accept our inner illumination as well. If truth be told (and it shall be), it can often be easier to accept the Beautiful Dark than to bathe in the Brilliance of the Light. The Light gives us nowhere to hide. We are ultimately vulnerable before It, obliterated by Its beneficence. Now that’s scary.
 Happily, our Goddess—while She is quite at home in the dark—is also a Lady of Light. And though She is quite capable of obliterating us with beneficence, She can also offer us Her Light as the spring sun offers its warm and persuasive light to the seeds and roots that are just now awakening in the muddy earth.
Happily, our Goddess—while She is quite at home in the dark—is also a Lady of Light. And though She is quite capable of obliterating us with beneficence, She can also offer us Her Light as the spring sun offers its warm and persuasive light to the seeds and roots that are just now awakening in the muddy earth.
Isis is associated with all the heavenly lights—as you likely know. Our Goddess is indeed a Sun Goddess. She is also seen in the light of Her holy star, Sirius, and even in the light of the moon, at least in later periods.

A festival calendar from the temple of Edfu records a summer procession of Isis the Brilliant. During that festival, the image of the radiant Goddess was carried among the people in Her sacred boat, coming to rest in Her boat-sanctuary. There, the calendar text tells us “every kind of good thing is offered to her.” Some modern Kemetic Orthodox groups celebrate this as the Aset Luminous Festival. Participants illuminate paper boats with candles and set them adrift to carry worshippers’ prayers to Isis. In accordance with the ancient traditions, offerings are also given to Isis at this time.
Isis’ temples in Italy may have been particularly well lit. Fifty-eight lamps were found in the temple at Pompeii. In that not-overly-large temple space, that many lamps would have provided a great deal of light. A personal Isis shrine in Pompeii had 20 lamps. Lamps were common votive gifts to Isis as well. In his ancient novel, The Golden Ass, Apuleius describes the lanterns, torches, candles, and “other kinds of artificial light” that were carried in a procession for Isis.

Surely not all of this illumination was purely practical. Indeed, Apuleius notes that the processional lights were symbols of the heavenly light of the stars in the Goddess’ heaven. He also uses many allusions to light and radiance in telling his readers about Isis. For example, the blessings brought by Isis are described as “radiant” (inlustre). The initiating priest in Apuleius’ story says that, unlike blind Fortune, Isis sees and “illumines the other gods too with the radiance of her light.”
It is also possible that Roman-period priests of Isis may have carried lighted lamps about in daylight as a symbol of the spiritual light bestowed by their Goddess. Seneca mentions a “linen-clad old man” (Isian clergy were notorious wearers of linen) who carried around a lighted lamp in broad daylight. J. Gwyn Griffiths, one of my favorite Isis scholars, thinks this may refer to a priest of Isis.
Just as light can literally dispel darkness, it is frequently a symbol of dispelling spiritual darkness. The Light of Isis illuminates the dark corners of our souls and shines light on our paths as we seek to understand the Divine Mystery. With our ancient sisters and brothers—initiates of the Mysteries of Isis—we can understand that the Light of Isis can help us grow in the brilliant Light of Her love, wisdom, and protection.
The Magic of the Hair of Isis
We are not immune to the charms of a beautiful head of hair and the ancient Egyptians weren’t either.
But they took appreciation for hair, especially feminine hair, to a whole new level of magnitude. For them, hair was magical. And, of course, Who would have the most magical hair of all? The Goddess of Magic: Isis Herself.
I have always understood that the long hair of Isis in Egyptian tradition—disarrayed and covering Her face in mourning or falling in heavy, dark locks over Her shoulders—to be the predecessor of the famous Veil of Isis of later tradition. Ah, but there is so much more.
In ancient Egypt, it was a mourning custom for Egyptian women to dishevel their hair. They wore it long and unkempt, letting it fall across their tear-stained faces, blinding them in sympathy with the blindness first experienced by the dead. As the Ultimate Divine Mourner, this was particularly true of Isis. At Koptos, where Isis was notably worshipped as a Mourning Goddess, a healing prayer made “near the hair at Koptos” is recorded. Scholars consider this a reference to Mourning Isis with Her disheveled and powerfully magical hair.

It is in Her disheveled, mourning state, that Isis finally finds Osiris. She reassembles Him, fans life into Him, and makes love with Him. As She mounts His prone form, Her long hair falls over Their faces, concealing Them like a veil and providing at least some perceived privacy for Their final lovemaking. As the Goddess and God make love, the meaning of Isis’ hair turns from death to life. It becomes sexy—remember those big-haired “paddle doll” fertility symbols?

This pairing of love and death is both natural and eternal. How many stories have you heard—or perhaps you have a personal one—about couples making love after a funeral? It’s so common that it’s cliché. But it makes perfect sense: in the face of death, we human beings must affirm life. We do so through the mutual pleasure of sex and, for heterosexual couples, the possibility of engendering new life that sex provides. The lovemaking of Isis and Osiris is the ultimate expression of this. Chapter 17 of the Book of Coming Forth by Day (aka the Book of the Dead), describes the disheveled hair of Isis when She comes to Osiris:
“I am Isis, you found me when I had my hair disordered over my face, and my crown was disheveled. I have conceived as Isis, I have procreated as Nephthys.” (Chapter 17; translation by Rosa Valdesogo Martín, who has extensively studied the connection of hair to funerary customs in ancient Egypt.)
There is also a variant of this chapter that has Isis apparently straightening up Her “bed head” following lovemaking:
“Isis dispels my bothers (?) [The Allen translation has “Isis does away with my guard; Nephthys puts an end to my troubles.]. My crown is disheveled; Isis has been over her secret, she has stood up and has cleaned her hair.” (Chapter 17 variant, translation by Martín, above.)
This lovemaking of Goddess and God has cosmic implications for its result is a powerful and important new life: Horus. As the new pharaoh, Horus restores order to both kingdom and cosmos following the chaos brought on by the death of the old pharaoh, Osiris.
Not only is hair symbolic of the blindness of death and the new life of lovemaking; the hair of the Goddesses is actually part of the magic of rebirth. Isis and Her sister, Nephthys, are specifically called the Two Long Haired Ones. The long hair of the Goddesses is associated with the knotting, tying, wrapping, weaving, knitting, and general assembling necessary to bring about the great Mystery of rebirth. Hair-like threads of magic are woven about the deceased who has returned to the womb of the Great Mother. The Coffin Texts give the name of part of the sacred boat of the deceased (itself a symbolic womb) as the Braided Tress of Isis.

In some Egyptian iconography, we see mourning women, as well as the Goddesses Isis and Nephthys, with hair thrown forward in what is known as the nwn gesture. Sometimes they/They actually pull a lock of hair forward, especially toward the deceased, which is called the nwn m gesture. It may be that this gesture, especially when done by Goddesses, is meant to transfer new life to the deceased, just as Isis’ bed-head hair brought new life to Osiris. It is interesting to note that the Egyptians called vegetation “the hair of the earth” and that bare land was called “bald” land, which simply reiterates the idea of hair is an expression of life.
Spell 562 of the Coffin Texts notes the ability of the hair of Isis and Nephthys to unite things, saying that the hair of the Goddesses is knotted together and that the deceased has come to “be joined to the Two Sisters and be merged in the Two Sisters, for they will never die.”

The Pyramid Texts instruct the resurrected dead to loosen their bonds, “for they are not bonds, they are the tresses of Nephthys.” Thus the magical hair of the Goddesses is only an illusory bond. Their hair is not a bond of restraint but rather the bonding agent needed for rebirth. Like the placenta that contains and feeds the child but is no longer necessary when the child is born, the reborn one throws off the tresses of the Goddesses that had previously wrapped her or him in safety.
The Egyptian idea of Isis as the Long-Haired One carried over into Her later Roman cult, too. In Apuleius’ account of the Mysteries of Isis, he describes the Goddess as having long and beautiful hair. Her statues often show Her with long hair, and Her priestesses were known to wear their hair long in honor of their Goddess.

This little bit of research has inspired me to want experiment with the magic of hair in ritual. In Isis Magic, the binding and unbinding of the hair is part of the “Lamentations of Isis” rite (where it is very powerful, I can tell you from experience), but I want to try using it in some solitary ritual, too. I have longish hair, so that will work, but if you don’t and are, like me, inspired to experiment, try using a veil. It is most certainly in Her tradition. (See “Veil” in my Offering to Isis.)
If you want to learn more about the traditions around hair and death, please visit Rosa Valdesogo Martín’s amazing and extensive site here. That’s where most of these images come from…many of which I had not seen before. Thank you, Rosa!
Isis & Min
I’m so used to thinking of Isis with Osiris that I can forget She is also paired with other Gods. Today, we’ll look at one of Them: the God of the Upright Phallus, Min.
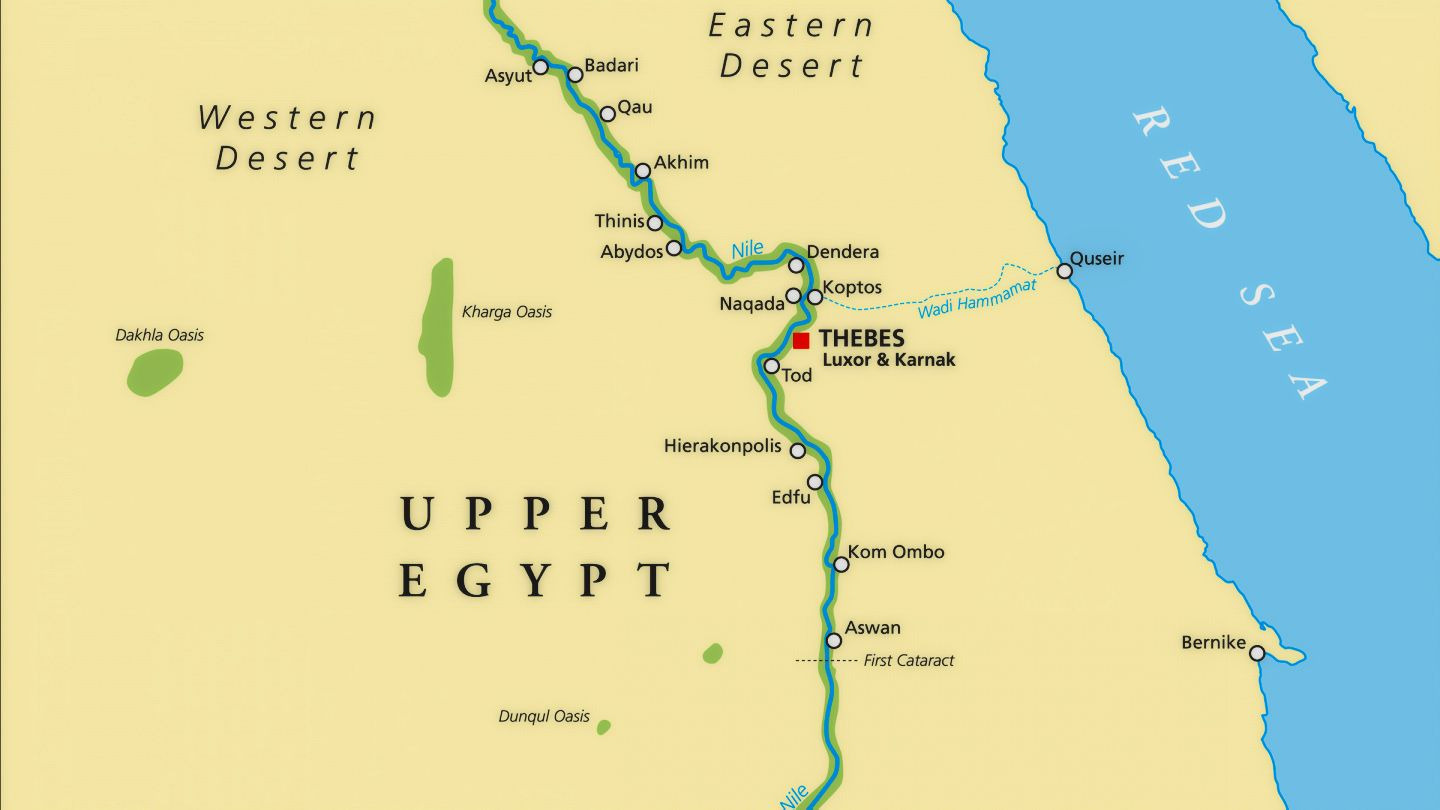
Isis and Min shared a temple complex at Koptos (Gebtu in ancient Egyptian, Qift in modern). It is in Upper Egypt, near Denderah and Thebes. The site is connected to the Red Sea by the Wadi Hammamat (meaning “Valley of Many Baths), a dry riverbed. The wadi contains important 3,000-year-old petroglyphs; in ancient times, it led to major Egyptian mining areas and was a key trade route.
Koptos is also just across the Nile from Naqada, the site of the pre-dynastic culture that takes its name from the site. What is known as Naqada II (3500-3400 BCE) is the period to which the beautiful statuettes of the “Nile Goddess” or “Dancing Woman” are dated.

Koptos is an ancient, ancient sacred site and probably originally belonged to Min alone. Herodotus reports that the Egyptians considered Him their oldest Deity. Yet by at least the time of the New Kingdom, Isis is prominent there as well and Min becomes assimilated with Osiris. The temple to Isis and Min, the ruins of which we see today, was built under Ptolemy II, with additions made under succeeding pharaohs. There are remains of two more temples on the site. One is the Ptolemaic “middle temple” or “Osiris temple.” The other is a temple dedicated to Geb and Isis, probably begun under Nectanebo II and continued under the Ptolemies. There is literary evidence for a temple of Isis and Harpokrates, but its remains have not yet been found.
One of the interesting things about Koptos is that it was a popular oracular site. You can still see the small chamber to the rear of the Isis and Geb temple in which the entranced priest would sit to deliver the words of the Deity. This oracular chapel was built by Kleopatra VII (the famous one). The tradition of oracles at Koptos did not cease with the coming of Christianity. In a work called Theosophia, we have record of an oracle from Koptos that is ostensibly an Egyptian Pagan oracle, but since it discusses the unity of the Logos and the Father, a number of scholars think it was likely a Christian retrofit. Be that as it may, the point is that the tradition of oracles at Koptos was well established.

A particular Isiac relic at Koptos seems to have been a lock of Her hair. A Greek dedication to Her says it is “to the Great Goddess, Isis of the Hair.” We also have a record of a healing prayer made “near the hair at Koptos.” Plutarch explains the tradition for us, relating that when Isis first heard of the death of Osiris, She cut off a lock of Her hair and donned mourning dress. He notes that this is why the city there is called Koptos for some derive the name from Greek koptein, meaning “to deprive.” The cutting of hair is a Greek mourning tradition; Egyptian women simply wore theirs long and unkempt. (Read more about that tradition here.) Nevertheless, among both Greeks and Egyptians, Isis of Koptos was particularly known a Mourning Goddess.
The ancient Greek travel writer, Pausanias, in his Description of Greece, mentions Koptos as the site of a tragedy that befell a man who rashly entered Isis’ sanctuary there without a specific invitation from the Goddess:
I have heard a similar story from a man of Phoenicia that the Egyptians hold the feast for Isis at a time when they say she is mourning for Osiris. At this time the Nile begins to rise, and it is a saying among many of the natives that what makes the river rise and water their fields is the tears of Isis. At that time then, so said my Phoenician, the Roman governor of Egypt bribed a man to go down into the shrine of Isis in Koptos. The man dispatched into the shrine returned indeed out of it, but after relating what he had seen, he too, so I was told, died immediately. So it appears that Homer’s verse speaks the truth when it says that it bodes no good to man to see godhead face to face. (Pausanias, Book X, 32, 10-17.)
Koptos must have had strong magical connections as well. If you recall the story of Setna and the magic book, you may remember that the magic book so coveted by Naneferkaptah was to be found at the bottom of the Nile by Koptos.
At Koptos, Isis is sometimes the mother of Min or Min-Hor, sometimes His consort. When Isis and Min are consorts, Min is the father of Hor-pa-khred, Horus the Child. Min is very much a God of male sexual prowess and thus, of course, fertility. Images of Him almost invariably show Him with an erect penis jutting out at an impressive right angle to His body. In the Coffin Texts, the deceased identified himself with “Woman-Hunting” Min to partake of His potent sexuality.
By the 18th dynasty, Min became associated with Amun and was incorporated into the festivals that were intended to revitalize the king. There is an ancient rite of Min called The Going Forth of Min and sometimes The Going Forth of Min to the Khedju, which may mean a type of ritual garden. During these festivals, the sacred image of the God was carried to a symbolic garden so that the God could bless the fields. This blessing was extended to the pharaoh; he took part in the procession as Horus, while the queen participated as Isis.
Although Min is usually shown in anthropomorphic form as a beautiful black man, at Koptos, He was also worshipped in the form of a white bull. Min is called the Beautiful Bull, the Strong Bull, and the Powerful Bull for the bull has always been a symbol of male strength and fertility.
He, Amun, and Horus are also known by the epithet, Kamutef, Bull of His Mother. The epithet has clear sexual connotations. Originally, it seems to have been an epithet of Horus, which was extended to Min when the two Gods were assimilated. It was further extended to Amun when He and Min were assimilated. It points to a primordial conception of the Divine in which the God is both son and lover of the Goddess. In a hymn to Min, a passage says:
Hail to Thee, Min, fecundating Thy mother; secret are Thy dealings with Her when the heavens are dark.
On a 13th dynasty stela, there is a similar inscription about Horus Kamutef:
Thy heart joins with the king as the heart of Horus joined with His mother Isis when He coupled with Her, flank to flank.
This ancient conception perfectly encapsulates the relationship between Isis and Min at Koptos. They are mother and son (sometimes Min is simply called “Min, Son of Isis” just as Horus is Harsiesis, “Horus, Son of Isis”) and They are lovers.
Min is usually shown with His legs tightly mummy-wrapped together but His penis exposed and ready. A flail is shown over His upraised right arm. The flail forms a “V” over His shoulder into the center of which the God places His upraised hand. Some have seen this as a sexual emblem: the vulva-triangle of the flail penetrated by the God’s penis-forearm. Sure, why not? I like it.

In addition to His bull epithets, Min is also known as Lord of Awe and Great of Love, just as Isis can be called Sweet of Love. (Perhaps She calls Him Lord of Awe at times when He has been particularly Great of Love.) In a hymn to Min from Koptos, He is said to love humankind and therefore He made youths (for fertile sex, of course). He is called Fair of Face and Sweet of Love. He is said to abominate the cutting short of the breath of life. He heals the sick and is “beautiful beyond the Gods.” He is also a Lunar God and Protector of the Moon.
I will admit that I have not, to date, done much to honor Min, perhaps because for me, that type of energy comes from Dionysos, to Whom I am also dedicated. Nevertheless, Isis and Min at Koptos make an intriguing pair. Isis is the Beautiful Mourner, the Goddess of the Disheveled Hair. Min is the Lord of Life Who invigorates human beings and agricultural fields alike. As Death and Life, They make a complete cycle. The Bull of His Mother brings renewal to Her in the form of Their Child. She, in turn, nurtures Him as Min, Son of Isis.
Isis & the Star of the New Year
Some people see Isis in the pale, magical light of the moon. Some see Her in the golden, life-giving rays of the sun. I do find Her there. Oh yes.

But for me, the heavenly body in which I most easily see Her is the star, Her star: Sirius (Sopdet in Egyptian, Sothis in Greek). I can’t help it. And it isn’t just because of Her strong ancient connections with the Fair Star of the Waters, the Herald of the Inundation. It’s something about the way my particular spiritual “stuff” fits with Her particular Divine “stuff.” Her diamond starlight draws me, lures me, illuminates my heart and mind.
I fell in love with Her as Lady of the Star the first time I saw Sirius through a telescope. As I watched, Her brilliant star sparkled with rays of green and blue and pink and white. It was incredibly, unutterably beautiful. It was alive. And pure.
The new year is a special time for those of us who find Isis in the light of Her star. Why so special? Because here in the Northern Hemisphere the Star of Isis reaches its highest point in the night sky at midnight on New Year’s Eve. This means that the Star of Isis can be our New Year’s Star just as the heliacal rising of Sirius was the Star of the New Year for the ancient Egyptians. I find that fact to be a small miracle, a gift of the Goddess that we can unwrap every New Year’s Eve. (For some Sirius science, look here.)
Likely, you already know why Sirius was important to the ancient Egyptians, so I won’t repeat that here. But I would like to add a few interesting bits about Sirius that I haven’t written about before; in particular, the orientation of some Egyptian temples and shrines to Sirius at the time of their construction. For instance, the small Isis temple at Denderah and Isis’ great temple at Philae seem to have been oriented toward the rising of Sirius. Philae may even have a double stellar orientation: one axis to the rising of Sirius, one to the setting of Canopus.
Overall, Egyptian temples have a variety of orientations. A survey team in 2004-2008 actually went to all the temples in Egypt and measured their orientations. They showed that most temples were oriented so that the main doorway faced the Nile. But not only that. It seems that the temples were also oriented toward other astronomical events, most especially the winter solstice sunrise, which makes very good sense as a symbol of rebirth.
Orientation to Sirius is rarer and harder to be certain of since the earth’s position in relation to the stars has shifted over the millennia.
A Horus temple, called the “Nest of Horus” on the summit of the highest peak of the Hills of Thebes, seems to have been oriented to the heliacal rising of Sirius around 3000-2000 BCE. Nearby, an inscription carved in rock during the 17th dynasty records the observation of just such a rising of Sirius. This high place would have been ideal for Horus in His nest to await the coming of His mother Isis. On the other hand, the archaeo-astronomers who did the survey I mentioned believe that it may also be oriented to the winter solstice sunrise, an event closely associated with Horus.
Another temple that may have a Sirius orientation is the archaic temple of the Goddess Satet on the island of Elephantine. The original temple was built amidst the great boulders on the island and really is quite simply the coolest temple ever. It seems that when it was built (around 3200 BCE) the rising of Sirius and the rising of the winter solstice sun were at the same place—so it could have been built to accommodate both important astronomical events.
After the initial study, the same team followed up with a survey (in 2008) of some temples in the Fayum that they hadn’t been able to study before as well as temples in Kush. They found generally the same results except for the Nile orientation as many of these temples were built far away from the river. They made note of a son of a Priest of Isis, Wayekiye, son of Hornakhtyotef, who was “hont-priest of Sothis (Sopdet) and wab-priest of the five living stars” (the planets) and “chief magician of the King of Kush;” this according to an inscription on Isis’ temple at Philae dating to about 227 CE. This emphasizes the importance and sacrality of the study of celestial objects and events to the kingdom and it is quite interesting that this was the work of the Chief Magician. This 2008 study revealed that the largest number of Kushite temples and pyramids were oriented to either the winter solstice sunrise or the rise of Sirius.
Another interesting thing the study found was that by the time of the New Kingdom, in the 34 temples that were unmistakably dedicated to a Goddess—specifically Isis or a Goddess identified with Her—the most important celestial orientation point was the rising of Sirius. But, in addition to Sirius, the star Canopus was also a key orientation point. According to their data, Goddess temples in general were more frequently aligned with these very bright stars, Sirius and Canopus, while God temples were more often oriented to key solar-cycle events.
The New Year has always been a time of reorientation and renewal, of oracles, portents, and purifications. As Sopdet, the Ba or Soul of Isis, shines down on us from its highest vantage point, now is a perfect time to undertake our own personal rites of renewal and reorientation. It is a time of clarity as we bathe in Her pure starlight, a time when we may ask for Her guidance. Whatever your favorite divination method, why not do a reading for the New Year now? Or, if you like a more ritualized oracle, try “The Rite of Loosing the Eyes” in Isis Magic. It is a winter rite in which you purify yourself and your temple, then ask Isis and Nephthys as the Eye Goddesses Who Go Forth to bring you news of what the New Year has in store.
Celebrating Where We Live
The Day of Sai Herthe, celebrated on the 7th Day of Nativity, is the Festival of Hearth and Home. Read about the traditions of the festival
Celebrating Where We Live
The Day of Sai Herthe, celebrated on the 7th Day of Nativity, is the Festival of Hearth and Home. Read about the traditions of the festival
The Lady of Heaven is Born
 Best wishes for Nativity! After the star brings the children of earth to the cave where the Daughter is born, and the princesses present their gifts, a beautiful voice fills the air, saying:
Best wishes for Nativity! After the star brings the children of earth to the cave where the Daughter is born, and the princesses present their gifts, a beautiful voice fills the air, saying:
Her Name shall be called Inanna
For She shall be Lady of Heaven
And the star vanished from the sky and yet its light remained. And the shape of the light became a vision. And the vision was a vision of the Mistress of All Things, bearing in Her arms the Holy Child.
Read all about the Nativity of God the Daughter



































