According to Herodotus, the Egyptians never sacrifice cows…
“…for these are sacred to Isis. For the image of Isis is always made in the form of a woman with the horns of an ox, as Io is pictured by the Greeks; and for that reason all Egyptians are alike in treating cows far more holy than other beasts.”
Who is Io and how is she (or She?) connected to Isis?
The story of Io is a Greek myth and apparently an ancient one. Here’s the tale:
Io was a priestess of Hera, even the first priestess of Hera, having established the Goddess’ worship in Argos. Io is also a naiad or water nymph, daughter of the River God, Inakhos.
Theoi.com (a wonderful mythology website) tells us that Io, in the Argive dialect, means “moon.” Other scholars have speculated that Io was a Hellenized version of an Egyptian word for both moon and Moon God, Iah.
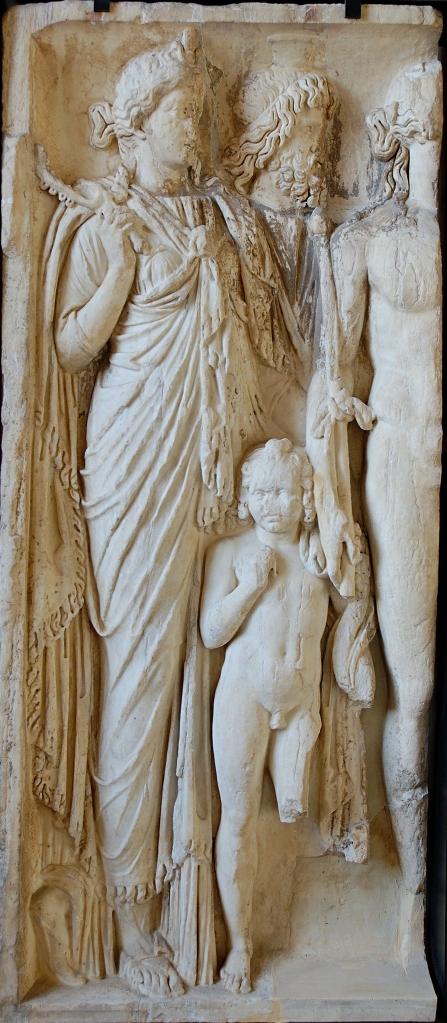
In the image above (you can click it to see it larger), from Pompeii’s Temple of Isis, we can see that the woman on the left does indeed have horns as in Herodotus’ description, although Isis, on the right with the cobra, does not. Judging by the details in this painting, it appears the Italian Isiacs were trying to maintain the Egyptian flavor of their rites. Note the diaphanous nature of Isis’ robe, as well as the breast-baring robe of the (probably) priestess behind Her, who holds a sistrum. Another figure, probably a priest, holds a sistrum, wand, and situla.
It seems more than likely that the artist was depicting the Isiac priestess and priest as he had seem them in the temple of Isis.
Anyway, back to our story. Hera’s ever-unfaithful husband, Zeus, falls in love with the lovely lunar nymph Io—either because of her great beauty or due to the spells of a iynx (a magical wheel sacred to Hekate; also known as Hekate’s Top or Wheel).
Io, meanwhile, had dreams that told her she should indeed surrender to Zeus, but when she told her father about them, he decided a second opinion was in order. Yet after consulting the Delphic oracle and the oracle of Dodona (an oracle of Zeus, by the way, so…), the answer remained the same. Thus, Io went secretly to Zeus and they made love. Now betrayed not only by Her husband but also by Her priestess, Hera was, to say the least, not pleased.
To protect Io from Hera’s anger, Zeus turned her into a beautiful white cow. Hera, pretending ignorance of the true identity of the lovely cow, promptly demanded that Zeus give the cow to Her. He could do nothing but comply. To guard Her new possession, Hera brought in Argos, Who had a hundred watchful eyes. Due to His many eyes, Argos was able to keep permanent vigil and was therefore a formidable guardian. But Zeus enlisted the aid of Hermes to help Io escape, which He finally did by killing Argos.
Io, still in the form of a cow, made good her escape, so Hera sent a horsefly or gadfly to torment her until she was driven mad. As a mad cow, she wandered and wandered across the world. In her wanderings, she gave her name to many geographic features. For instance, the Ionian Sea is supposed to be named for her. Finally, the white cow, Io, arrives in Egypt.
There she regained her human form—Aeschylus says Zeus healed her—and bore Zeus’ son, Epaphus. Herodotus gives Epaphus as an alternative name for the Egyptian Apis bull. (Some of you may remember that the Isis-cow is the one who gives birth to the Apis bull.)
Other stories have Io, already in human form, kidnapped by Phoenicians or pirates, and brought to Egypt. But Io’s troubles are not yet over, for Hera next ordered the Kouretes (young Divine warriors Who serve the Mother Goddess) to kidnap Epaphus—so once again, Io wandered, this time, searching for her lost son. At last, she learned that the queen of Byblos was raising Epaphus. Io went to Byblos and eventually returned with Epaphus to Egypt where, according to Apollodorus, Io “dedicated an image to Demeter, called Isis by the Aigyptians, as also they called Io herself.”
Despite a few Egyptian-ish details in Io’s tale, Io’s connection with Isis, or even identification with Her, may, at first, be a bit puzzling. Yet, there are a number of correspondences between Isis and Io. The theme of searching for a loved one, pursued by an enemy is common to both. In fact, both wander twice. Both appear as white cows. Both are associated with the moon. Both are aided by the God of Knowledge; Hermes in the case of Io, Thoth in the case of Isis. In Plutarch’s later version of the Isis-Osiris myth, Isis finds Osiris’ body in Byblos. Io finds her son in Byblos. And in Apuleius’ tale of initiation into Isis’ Mysteries, the theme of being returned to human form after suffering trials in the form of an animal applies to Lucius in Apuleius’ tale and to Io in Her many myths. A 10th century CE lexicon or encyclopedia, known as the Suda (or Suidas), makes the identification complete under the entry for Isis:
Isis: She is called Io. She was snatched by Zeus from Argos and he, fearing Hera, changed her first into a white cow, then into a black one, and then into a one that was violet-coloured. After wandering around with her, he came into Egypt. The Egyptians, then, honour Isis, and for this reason they carve the horns of a cow on the head of her statue, alluding to the change from maiden to cow.

It is always interesting to me that when we first see the connections drawn by the ancients between the Deities (for Io becomes a Goddess), we can, at first, find them to be something of a stretch.
Yet if we follow the trail a bit more, the associations become much less strained. Io is certainly a case in point. When we look deeper into the myths and stories, we find the holy correspondences. We see the sacred connections. We glimpse a little more of the Divine interweavings that underlie and interpenetrate all things.
NOTE: It turns out that Io was one of the most frequently cited identifications with Isis in Roman literature. In other words, they were understanding Isis through the story of Io. Some of the Roman poets, separated from their lovers by the Isiac requirement for sexual abstinence before specific rites, complained rather bitterly about said separations. And to tell the truth, they were kinda jerks about it.